A computational model of ureteral peristalsis and an investigation into ureteral reflux
- PMID: 30603196
- PMCID: PMC6208564
- DOI: 10.1007/s13534-017-0053-0
A computational model of ureteral peristalsis and an investigation into ureteral reflux
Abstract
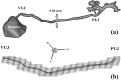
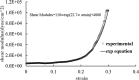
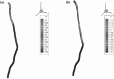
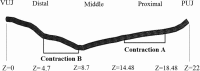
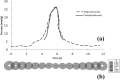
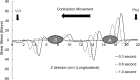
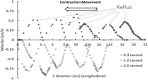
The aim of this study is to create a computational model of the human ureteral system that accurately replicates the peristaltic movement of the ureter for a variety of physiological and pathological functions. The objectives of this research are met using our in-house fluid-structural dynamics code (CgLes-Y code). A realistic peristaltic motion of the ureter is modelled using a novel piecewise linear force model. The urodynamic responses are investigated under two conditions of a healthy and a depressed contraction force. A ureteral pressure during the contraction shows a very good agreement with corresponding clinical data. The results also show a dependency of the wall shear stresses on the contraction velocity and it confirms the presence of a high shear stress at the proximal part of the ureter. Additionally, it is shown that an inefficient lumen contraction can increase the possibility of a continuous reflux during the propagation of peristalsis.
Keywords: CFD; PUJ; Reflux; Ureter; VUJ; VUR.
Conflict of interest statement
None.All scans showing the whole ureter with normal anatomy were anonymised and chosen at random from a larger educational set.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Three-Dimensional Numerical Simulations of Peristaltic Contractions in Obstructed Ureter Flows.J Biomech Eng. 2016 Oct 1;138(10). doi: 10.1115/1.4034307. J Biomech Eng. 2016. PMID: 27464354
-
A mathematical simulation of the ureter: effects of the model parameters on ureteral pressure/flow relations.J Biomech Eng. 2011 Mar;133(3):031004. doi: 10.1115/1.4003316. J Biomech Eng. 2011. PMID: 21303180
-
A two-dimensional numerical study of peristaltic contractions in obstructed ureter flows.Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2018 Jan;21(1):22-32. doi: 10.1080/10255842.2017.1415333. Epub 2017 Dec 22. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2018. PMID: 29271257
-
Ureteral motility.Acta Physiol Hung. 2009 Dec;96(4):407-26. doi: 10.1556/APhysiol.96.2009.4.2. Acta Physiol Hung. 2009. PMID: 19942548 Review.
-
Physiopathology of vesico-ureteral reflux.Ital J Pediatr. 2016 Nov 29;42(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s13052-016-0316-x. Ital J Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 27899160 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Peristaltic channel flow and heat transfer of Carreau magneto hybrid nanofluid in the presence of homogeneous/heterogeneous reactions.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 13;10(1):11499. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-68409-0. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32661273 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Prototypable Biomimetic Peristalsis Bioreactor Capable of Concurrent Shear and Multi-Axial Strain.Cells Tissues Organs. 2023;212(1):96-110. doi: 10.1159/000521752. Epub 2022 Jan 10. Cells Tissues Organs. 2023. PMID: 35008089 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wein AJ, Kavoussi L, Partin W, Peters CA. Urology, Campbell-Walsh. Vol. 2 of section XIV. 2012.
-
- Weiss RM, Wagner ML, Hoffman BF. Localization of the pacemaker for peristalsis in the intact canine ureter. Invest Urol. 1967;5(42):1.
-
- Watanabe H, Nakagawa Y, Uchida M. Tests to evaluate the mechanical properties of the ureter. In: Kambic HE, Yokobori AT, editors. Biomaterials’ mechanical properties. ASTM International; 1994.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
