Photoacoustic microscopy: principles and biomedical applications
- PMID: 30603203
- PMCID: PMC6208522
- DOI: 10.1007/s13534-018-0067-2
Photoacoustic microscopy: principles and biomedical applications
Abstract
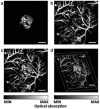
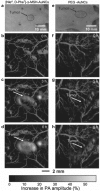
Photoacoustic microscopy (PAM) has become an increasingly popular technology for biomedical applications, providing anatomical, functional, and molecular information. In this concise review, we first introduce the basic principles and typical system designs of PAM, including optical-resolution PAM and acoustic-resolution PAM. The major imaging characteristics of PAM, i.e. spatial resolutions, penetration depth, and scanning approach are discussed in detail. Then, we introduce the major biomedical applications of PAM, including anatomical imaging across scales from cellular level to organismal level, label-free functional imaging using endogenous biomolecules, and molecular imaging using exogenous contrast agents. Lastly, we discuss the technical and engineering challenges of PAM in the translation to potential clinical impacts.
Keywords: Endogenous biomolecules; Exogenous contrast agents; Functional imaging; Molecular imaging; Photoacoustic microscopy; Structural imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Figures

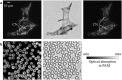
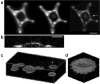
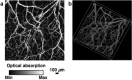
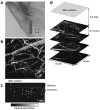
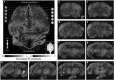
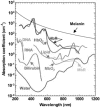
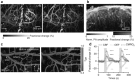
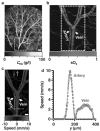
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
