A pilot study of short-term toe resistance training in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 30603345
- PMCID: PMC6224917
- DOI: 10.1007/s13340-017-0318-y
A pilot study of short-term toe resistance training in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this pilot study was to investigate the effect of short-term toe resistance training on toe pinch force and toe muscle quality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods: A total of 12 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who were hospitalized to improve glycemic control (8 men and 4 women, duration of diabetes 12.2 ± 9.5 years) were enrolled in this pilot study. Exercise therapy was performed with conventional aerobic exercise and four newly developed toe resistance training exercises for 2 weeks. Changes in anthropometric parameters, blood pressure (BP), heart rate, and muscle parameters, i.e. muscle mass, toe pinch force and toe muscle quality were evaluated after the exercise program.
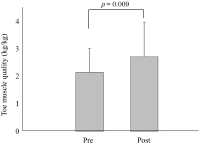
Results: There were no significant differences of body weight, body mass index, BP, heart rate, and upper/lower muscle mass after exercise performance. However, toe pinch force was significantly increased (pre: 2.92 ± 1.19 kg, post: 3.65 ± 1.58 kg, p = 0.007). Toe muscle quality (toe pinch force/lower leg muscle mass) were also significantly increased (pre: 2.15 ± 0.86 kg/kg, post: 2.72 ± 1.26 kg/kg, p = 0.009).
Conclusions: Two weeks of toe resistance training significantly increased toe pinch force and toe muscle quality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Toe resistance training is might be essential for treating patients with diabetes mellitus in clinical practice.
Keywords: Toe muscle quality; Toe pinch force; Toe resistance training; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no financial support or relationships that could pose a conflict of interest.All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and later versions. Informed consent or substitute for it was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Efficacy of Short-Term Toe Resistance Training in Chronic Hemodialysis Patients with Type 2 Diabetes.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Jan 1;11(1):137. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11010137. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36611597 Free PMC article.
-
A Randomized Controlled Trial of Short-term Toe Resistance Training to Improve Toe Pinch Force in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes.Acta Med Okayama. 2018 Feb;72(1):9-15. doi: 10.18926/AMO/55657. Acta Med Okayama. 2018. PMID: 29463933 Clinical Trial.
-
Relationship of toe pinch force to other muscle strength parameters in men with type 2 diabetes.Environ Health Prev Med. 2016 Jul;21(4):179-85. doi: 10.1007/s12199-016-0512-8. Epub 2016 Feb 15. Environ Health Prev Med. 2016. PMID: 26879315 Free PMC article.
-
Role of exercise training in the prevention and treatment of insulin resistance and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.Sports Med. 1997 Nov;24(5):321-36. doi: 10.2165/00007256-199724050-00004. Sports Med. 1997. PMID: 9368278 Review.
-
Association Between Physical Exercise Interventions Participation and Functional Capacity in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Controlled Trials.Sports Med Open. 2022 Mar 4;8(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s40798-022-00422-1. Sports Med Open. 2022. PMID: 35244804 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Efficacy of Short-Term Toe Resistance Training in Chronic Hemodialysis Patients with Type 2 Diabetes.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Jan 1;11(1):137. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11010137. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36611597 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of exercise prescription into medical provision as a treatment for non-communicable diseases: A scoping review.Front Public Health. 2023 Jul 12;11:1126244. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1126244. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37501942 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes Mellitus-Related Dysfunction of the Motor System.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 11;21(20):7485. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207485. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33050583 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kataoka H, Ishikawa I, Hayashino S, Yamanoto K, Miyazawa Y, Tanaka S, et al. Reproducibility of toe pinch dynamometer procedure. J Dist Environ Health Welf Res. 2015;18:39–44.
-
- Kataoka H, Miyatake N, Kitayama N, Murao S, Tanaka S Toe pinch force in male type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Acta Med Okayama (in press). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
