Factors involved in decreasing the therapeutic effect of sitagliptin: a subanalysis of the JAMP study
- PMID: 30603363
- PMCID: PMC6224911
- DOI: 10.1007/s13340-017-0340-0
Factors involved in decreasing the therapeutic effect of sitagliptin: a subanalysis of the JAMP study
Abstract
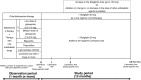
Objective: As a subanalysis of the Januvia Multicenter Prospective Trial in Type 2 Diabetes (JAMP study), we examined factors that decreased blood glucose control effect of sitagliptin after 3 months and patients requiring an addition or increase of diabetes treatment.
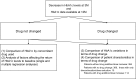
Methods: We selected patients in whom glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels decreased by month 3 after initiation of sitagliptin treatment and conducted two analyses: (1) in patients who did not change drugs until month 12, we compared changes in HbA1c levels between concomitant drugs and examined factors that decreased blood glucose control effect of sitagliptin; (2) compared changes in HbA1c levels and backgrounds between patients who did and did not require an addition to or increased dose of the antidiabetic agent.
Results: Four hundred and ninety-eight patients were chosen. In 369 patients without drug change until month 12, changes in HbA1c levels during months 3-12 were not significantly different among concomitant drugs; factors causing rebound HbA1c were smoking and weight gain. Patient characteristics were compared between those who did and did not require an additional drug or a dose increase (n = 114) (n = 384). Drug changes were associated with longer disease duration, younger age, higher rate of smoking, and higher degree of insulin resistance but not with concomitantly administered drugs.
Conclusion: Smoking and weight gain were factors that decreased the effect of sitagliptin on reducing blood glucose levels. Differences in concomitant drugs did not affect sitagliptin's effects on glycemic control. A dose increase or the addition of the antidiabetic drug was not associated with concomitant drugs.
Keywords: DPP4-inhibitor; Decreasing the therapeutic effect; HbA1c rebound factor; Sitagliptin; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
Hiroshi Sakura received honoraria from Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation and research grant from Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and later versions. The ethics committee at the Tokyo Women’s Medical University approved the study (Approval Number: 2064) on 11 January 2011. Informed consent or substitute was obtained from all patients included in the study.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and comparison of hypoglycemic action of concomitant medications: a subanalysis of the JAMP study.Diabetol Int. 2017 Jul 28;9(1):56-65. doi: 10.1007/s13340-017-0330-2. eCollection 2018 Feb. Diabetol Int. 2017. PMID: 30603350 Free PMC article.
-
Factor Analysis of Changes in Hemoglobin A1c After 12 Months of Sitagliptin Therapy in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes.J Clin Med Res. 2016 Jun;8(6):461-71. doi: 10.14740/jocmr2540w. Epub 2016 May 25. J Clin Med Res. 2016. PMID: 27222674 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Predicting Therapeutic Efficacy of Combination Treatment With Sitagliptin and Insulin in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: The ASSIST-K Study.J Clin Med Res. 2015 Aug;7(8):607-12. doi: 10.14740/jocmr2149w. Epub 2015 Jun 9. J Clin Med Res. 2015. PMID: 26124906 Free PMC article.
-
Factors associated with reduced efficacy of sitagliptin therapy: analysis of 93 patients with type 2 diabetes treated for 1.5 years or longer.J Clin Med Res. 2013 Jun;5(3):217-21. doi: 10.4021/jocmr1256w. Epub 2013 Apr 23. J Clin Med Res. 2013. PMID: 23671547 Free PMC article.
-
Sitagliptin: a novel drug for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.Cardiol Rev. 2007 Sep-Oct;15(5):264-71. doi: 10.1097/CRD.0b013e318123f771. Cardiol Rev. 2007. PMID: 17700385 Review.
References
-
- Ku EJ, Jung KY, Kim YJ, Kim KM, Moon JH, Choi SH, Cho YM, Park KS, Jang HC, Lim S, Ahrén B. Four-year durability of initial combination therapy with sitagliptin and metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes in clinical practice; COSMIC study. PLoS ONE. 2015 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129477. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
