Current Status of Stem Cell Treatment for Type I Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 30603589
- PMCID: PMC6250656
- DOI: 10.1007/s13770-018-0143-9
Current Status of Stem Cell Treatment for Type I Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
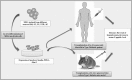
Background: Diabetes mellitus is a major health concern in current scenario which has been found to affect people of almost all ages. The disease has huge impact on global health; therefore, alternate methods apart from insulin injection are being explored to cure diabetes. Therefore, this review mainly focuses on the current status and therapeutic potential of stem cells mainly mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) for Type 1 diabetes mellitus in preclinical animal models as well as humans.
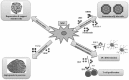
Methods: Current treatment for Type 1 diabetes mellitus mainly includes use of insulin which has its own limitations and also the underlying mechanism of diseases is still not explored. Therefore, alternate methods to cure diabetes are being explored. Stem cells are being investigated as an alternative therapy for treatment of various diseases including diabetes. Few preclinical studies have also been conducted using undifferentiated MSCs as well as in vitro MSCs differentiated into β islet cells.
Results: These stem cell transplant studies have highlighted the benefits of MSCs, which have shown promising results. Few human trials using stem cells have also affirmed the potential of these cells in alleviating the symptoms.
Conclusion: Stem cell transplantation may prove to be a safe and effective treatment for patients with Type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Keywords: Bone marrow; Diabetes mellitus; In vitro differentiation; Stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.There are no animal expreiments carried out for this article.
Figures
References
-
- IDF Diabetes Atlas, 5th edition. International Diabetes Federation. 2011. https://www.idf.org/our-activities/advocacy-awareness/resources-and-tool....
-
- Atkinson MA, Eisenbarth GS. Type I diabetes: new perspectives on disease pathogenesis and treatment. Lancet. 2001;358:221–229. - PubMed
-
- DeFronzo RA. Pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes: metabolic and molecular implications for identifying diabetes genes. Diabetes Rev. 1997;5:177–266.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
