A young man with an unchanged consolidation in chest CT
- PMID: 30603607
- PMCID: PMC6307102
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2018.12.008
A young man with an unchanged consolidation in chest CT
Abstract
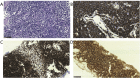
Primary pulmonary mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma is extremely rare. MALT lymphoma patients usually show no clinical symptoms or physical signs. Chest radiograph or computed tomography (CT) may confuse MALT lymphoma with other pulmonary diseases, which would lead to misdiagnosis or a delayed diagnosis. In the present study, a 33-year-old male patient had cough and fever. Chest CT showed consolidation on both sides. Those clinical symptoms disappeared after he had been misdiagnosed and treated for community-acquired pneumonia for three weeks. However, further chest CT still showed the consolidation without any change. Then an ultrasonic guided transthoracic needle biopsy was performed. Morphological changes indicated the diagnosis of extranodal marginal Zone B cell lymphoma of MALT. The patient was then treated with chemotherapy and rituximab. After this line of treatment, the consolidation decreased.
Keywords: Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue; Primary pulmonary lymphoma; Unchanged consolidation.
Figures

References
-
- Kim J.H., Lee S.H., Park J., Kim H.Y., Lee S.I., Park J.O., Kim K., Kim W.S., Jung C.W., Park Y.S., Im Y.H., Kang W.K., Lee M.H., Park K., Han J.H., Ko Y.H. Primary pulmonary non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004;34:510–514. - PubMed
-
- Harris N.L., Jaffe E.S., Diebold J., Flandrin G., Muller-Hermelink H.K., Vardiman J., Lister T.A., Bloomfield C.D. The world health organization classification of hematological malignancies report of the clinical advisory committee meeting, airlie house, Virginia, November 1997. Mod. Pathol. 2000;13:193–207. - PubMed
-
- Cohen S.M., Petryk M., Varma M., Kozuch P.S., Ames E.D., Grossbard M.L. Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. Oncologist. 2006;11:1100–1117. - PubMed
-
- Verma V.J., Jain S., Singhal S., Nallagatla S., Majumdar A., Vangala M., Arjomand F., Vasudevan V.P. Primary pulmonary mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma in a patient with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Respir. Care. 2011;56:1046–1049. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

