Retrospective study on the effects of the prognosis of patients treated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation combined with continuous renal replacement therapy
- PMID: 30603643
- PMCID: PMC6312806
- DOI: 10.21037/atm.2018.11.12
Retrospective study on the effects of the prognosis of patients treated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation combined with continuous renal replacement therapy
Abstract
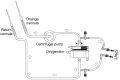
Background: Patients undergoing extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) treatment often have severe fluid overload and electrolyte imbalances and may even suffer acute kidney injury (AKI). It is often necessary to use continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT). In this study, we aimed to retrospectively analyze the prognosis of patients treated with ECMO combined with CRRT and to find the independent factors that affect the survival rate.
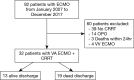
Methods: There were 32 patients who were treated with ECMO combined with CRRT in our hospital from January 2007 to December 2017 who were analyzed. All of the patients were divided into a survival group and death group. The clinical indicators and biochemical indexes of the two groups were observed, and their differences were compared. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was carried out to determine the independent risk factors.
Results: The fluid balance at ECMO day 3, SOFA score and lactate at CRRT initiation, sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) score at ECMO weaning, CRRT duration, ECMO to CRRT interval, mechanical ventilation (MV) duration, length of ICU, and overall hospital length of stay were statistically significant (P<0.05). The clinical biochemical indexes at CRRT initiation and ECMO weaning [serum creatinine, pH, white blood cell (WBC), hemoglobin (Hb), bilirubin]; patient's age, gender and BMI; and the fluid balance at ECMO days 1 and 7 were not statistically significance (P>0.05). The fluid balance at ECMO day 3 and lactate at CRRT initiation by multivariable logistic regression analysis were independent risk factors affecting patient prognosis.
Conclusions: The fluid balance at ECMO day 3 and lactate at CRRT initiation are the prognosis independent risk factors for ECMO + CRRT patients.
Keywords: Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO); continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT); prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fluid overload and fluid removal in pediatric patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation requiring continuous renal replacement therapy: a multicenter retrospective cohort study.Pediatr Nephrol. 2020 May;35(5):871-882. doi: 10.1007/s00467-019-04468-4. Epub 2020 Jan 17. Pediatr Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 31953749 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes among Patients Treated with Renal Replacement Therapy during Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: A Single-Center Retrospective Study.Blood Purif. 2020;49(3):341-347. doi: 10.1159/000504287. Epub 2019 Dec 19. Blood Purif. 2020. PMID: 31865351 Free PMC article.
-
[Continuous renal replacement therapy combined with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for pediatric cardiopulmonary failure].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2018 May 2;56(5):336-341. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1310.2018.05.006. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29783818 Chinese.
-
Continuous renal replacement therapy in patients treated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.Semin Dial. 2021 Nov;34(6):537-549. doi: 10.1111/sdi.12965. Epub 2021 Mar 25. Semin Dial. 2021. PMID: 33765346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Managing the kidney - The role of continuous renal replacement therapy in neonatal and pediatric ECMO.Semin Pediatr Surg. 2023 Aug;32(4):151332. doi: 10.1016/j.sempedsurg.2023.151332. Epub 2023 Oct 17. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2023. PMID: 37871460 Review.
Cited by
-
Concurrent Use of Renal Replacement Therapy during Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Support: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Clin Med. 2021 Jan 11;10(2):241. doi: 10.3390/jcm10020241. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33440805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimising fluid therapy during venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: current evidence and future directions.Ann Intensive Care. 2025 Mar 19;15(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s13613-025-01458-8. Ann Intensive Care. 2025. PMID: 40106084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Incidence and Impact of Acute Kidney Injury in Patients Receiving Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: A Meta-Analysis.J Clin Med. 2019 Jul 5;8(7):981. doi: 10.3390/jcm8070981. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31284451 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of CRRT in Patients with PARDS Treated with VV-ECMO.Membranes (Basel). 2021 Mar 11;11(3):195. doi: 10.3390/membranes11030195. Membranes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33799847 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of renal complications on outcome in adult patients with acute fulminant myocarditis receiving venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: an analysis of nationwide CSECLS database in China.Ann Intensive Care. 2023 Sep 27;13(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s13613-023-01186-x. Ann Intensive Care. 2023. PMID: 37755544 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khwaja A. KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin Pract. 2012;120:c179-84. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
