Sequential and synchronized hypertonicity-induced activation of Rel-family transcription factors is required for osmoprotection in renal cells
- PMID: 30603705
- PMCID: PMC6304461
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e01072
Sequential and synchronized hypertonicity-induced activation of Rel-family transcription factors is required for osmoprotection in renal cells
Abstract
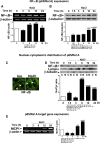
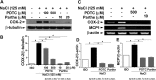
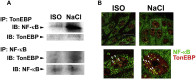
NF-κB and TonEBP belong to the Rel-superfamily of transcription factors. Several specific stimuli, including hypertonicity which is a key factor for renal physiology, are able to activate them. It has been reported that, after hypertonic challenge, NF-κB activity can be modulated by TonEBP, considered as the master regulator of transcriptional activity in the presence of changes in environmental tonicity. In the present work we evaluated whether hypertonicity-induced gene transcription mediated by p65/RelA and TonEBP occurs by an independent action of each transcription factor or by acting together. To do this, we evaluated the expression of their specific target genes and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), a common target of both transcription factors, in the renal epithelial cell line Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) subjected to hypertonic environment. The results herein indicate that hypertonicity activates the Rel-family transcription factors p65/RelA and TonEBP in MDCK cells, and that both are required for hypertonic induction of COX-2 and of their specific target genes. In addition, present data show that p65/RelA modulates TonEBP expression and both colocalize in nuclei of hypertonic cultures of MDCK cells. Thus, a sequential and synchronized action p65/RelA → TonEBP would be necessary for the expression of hypertonicity-induced protective genes.
Keywords: Biochemistry; Cell biology; Molecular biology.
Figures



References
-
- Dmitrieva N.I., Burg M.B. Hypertonic stress response. Mutat. Res. 2005;569:65–74. - PubMed
-
- Alfieri R.R., Petronini P.G. Hyperosmotic stress response: comparison with other cellular stresses. Pflügers Archiv. 2007;454:173–185. - PubMed
-
- Kwon M.S., Lim S.W., Kwon H.M. Hypertonic stress in the kidney: a necessary evil. Physiology. 2009;24:186–191. - PubMed
-
- Burg M.B. Molecular basis of osmotic regulation. Am. J. Physiol. 1995;268:F983–F996. - PubMed
-
- Burg M.B., Kwon E.D., Kultz D. Regulation of gene expression by hypertonicity. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1997;59:437–455. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

