Various salts employed as precipitant in combination with polyethylene glycol in protein/detergent particle association
- PMID: 30603706
- PMCID: PMC6307348
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e01073
Various salts employed as precipitant in combination with polyethylene glycol in protein/detergent particle association
Abstract
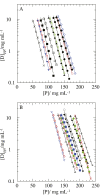
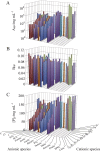
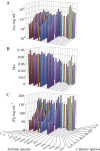
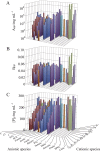
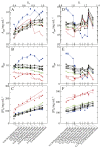
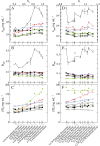
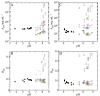
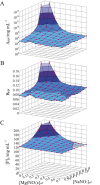
Salt/polyethylene glycol (PEG) mixtures are employed as precipitants for biological macromolecules. The dependence of precipitation curves (PCs) on salt species was investigated for integral membrane protein/detergent particles. By relating this dependence to properties of ions dissociated from added salts, the following roles and effects of various ions were clarified. In the presence of ions whose interaction with water is stronger than water-water interaction, the coordination of solvent molecules is rearranged so as to strengthen short-range steric repulsion and hydrophobic attraction. Ions whose interaction with water is weaker than water-water interaction can be a hindrance to hydrophobic-hydrophobic contact. Moreover, strong electric fields of divalent cations can cause an attractive effect between electronegative or polar groups of neighboring particles. The variations of particle-particle and particle-PEG interactions depending on the state of particles and surrounding solvents were correlative. Due to this, the relationship between the horizontal positions of PC and the species of salts added could be formulated as a binary linear function of cationic and anionic species composing the salts.
Keywords: Biochemistry; Inorganic chemistry; Physical chemistry.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intermolecular interactions at early stage of protein/detergent particle association induced by salt/polyethylene glycol mixtures.Protein Expr Purif. 2016 Apr;120:72-86. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2015.12.009. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Protein Expr Purif. 2016. PMID: 26705098
-
Long-range and short-range mechanisms of hydrophobic attraction and hydrophilic repulsion in specific and aspecific interactions.J Mol Recognit. 2003 Jul-Aug;16(4):177-90. doi: 10.1002/jmr.618. J Mol Recognit. 2003. PMID: 12898668 Review.
-
Data in support of intermolecular interactions at early stage of protein/detergent particle association induced by salt/polyethylene glycol mixtures.Data Brief. 2016 Apr 8;7:1283-7. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2016.04.003. eCollection 2016 Jun. Data Brief. 2016. PMID: 27135050 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of salt or cosolvent addition on solubility of a hydrophobic solute in water: Relevance to those on thermal stability of a protein.J Chem Phys. 2017 Feb 7;146(5):055102. doi: 10.1063/1.4975165. J Chem Phys. 2017. PMID: 28178788
-
Segregation of inorganic ions at surfaces of polar nonaqueous liquids.Chemphyschem. 2007 Jul 16;8(10):1457-63. doi: 10.1002/cphc.200700039. Chemphyschem. 2007. PMID: 17520587 Review.
References
-
- Juckes I.R.M. Fraction of proteins and viruses with polyethylene glycol. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1971;229:535–546. - PubMed
-
- McPherson A. The growth and preliminary investigation of protein and nucleic acid crystals for X-ray diffraction analysis. Methods Biochem. Anal. 1976;23:249–345. - PubMed
-
- Ingham K.C. Precipitation of proteins with polyethylene glycol: characterization of albumin. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1978;186:106–113. - PubMed
-
- Arakawa T., Timasheff S.N. Theory of protein solubility. Methods Enzymol. 1985;114:49–77. - PubMed
-
- Kühlbrandt W. Three–dimensional crystallization of membrane proteins. Q. Rev. Biophys. 1988;21:429–477. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

