Determination of lamotrigine in human plasma using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
- PMID: 30604456
- PMCID: PMC7292279
- DOI: 10.1002/npr2.12045
Determination of lamotrigine in human plasma using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
Abstract
Aim: Lamotrigine (LTG) is a widely used anti-epileptic drug that is administered to avoid seizures and to maintain seizure-free status. However, several factors reportedly cause individual differences of plasma LTG levels, and the therapeutic target range of LTG varies between individuals. Thus, to optimize effective doses of LTG, we developed a rapid and simple method for determining plasma LTG concentrations.
Methods: Lamotrigine and the internal standard papaverine were extracted from human plasma using solid-phase extraction. After filtration, 5-μL aliquots of final samples were injected into the liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry instrument and LTG and internal standard were separated using a Cadenza CD-C18 column (100 × 2 mm, 3 μm) with 0.1% formic acid in water/acetonitrile (2/1, v/v).
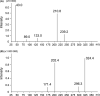
Results: The calibration curve was linear from 0.2 to 5.0 μg/mL, and assessments of recovery, intra- and inter-day precision and accuracy, matrix effects, freeze and thaw stability, and long-term stability demonstrated good reproducibility. Retention times of LTG and internal standard were 1.6 and 2.0 minutes, respectively, and the total run time was 3.5 minutes for each sample.
Conclusion: We developed a rapid and simple method for determining plasma LTG concentrations. The present novel system could be used to inform LTG dose adjustments for individual patients.
Keywords: epilepsy; lamotrigine; liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry; plasma concentration; solid-phase extraction.
© 2018 The Authors. Neuropsychopharmacology Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of The Japanese Society of Neuropsychopharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Froscher W, Keller F, Vogt H, Kramer G. Prospective study on concentration‐efficacy and concentration‐toxicity: correlations with lamotrigine serum levels. Epileptic Disord. 2002;4(1):49–56. - PubMed
-
- Brzakovic BB, Vezmar Kovacevic SD, Vucicevic KM, et al. Impact of age, weight and concomitant treatment on lamotrigine pharmacokinetics. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2012;37(6):693–7. - PubMed
-
- Baldoni AO, Freitas‐Lima P, de Santi Ferreira FI, et al. An investigation of the influence of patient‐related factors and comedications on lamotrigine clearance in patients with epilepsy. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016;43(7):685–9. - PubMed
-
- Liu L, Zhao L, Wang Q, Qiu F, Wu X, Ma Y. Influence of valproic acid concentration and polymorphism of UGT1A4*3, UGT2B7 ‐161C > T and UGT2B7*2 on serum concentration of lamotrigine in Chinese epileptic children. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2015;71(11):1341–7. - PubMed
-
- Inoue K, Yamamoto Y, Suzuki E, et al. Factors that influence the pharmacokinetics of lamotrigine in Japanese patients with epilepsy. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2016;72(5):555–62. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

