Application of the DILEMMA score to improve lesion selection for invasive physiological assessment
- PMID: 30604558
- PMCID: PMC6824904
- DOI: 10.1002/ccd.28054
Application of the DILEMMA score to improve lesion selection for invasive physiological assessment
Abstract
Objectives: We sought to assess the validity of the DILEMMA score against instantaneous wave-free ratio (iFR) and evaluate its utility in rationalizing the number of patients referred for invasive physiological assessment.
Background: The DILEMMA score is a validated angiographic scoring tool incorporating minimal lumen diameter, lesion length and subtended myocardial area that has been shown to predict the functional significance of lesions as assessed by fractional flow reserve (FFR).
Methods: Patients in the DEFINE-FLAIR study who had coronary stenosis of intermediate severity were randomized to either FFR or iFR. DILEMMA score was calculated retrospectively on a subset of this cohort by operators blinded to FFR or iFR values.
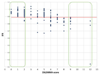
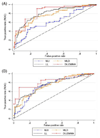
Results: Three hundred and forty-six lesions (181 assessed by FFR; 165 by iFR) from 259 patients (mean age 66.0 years, 79% male) were included. A DILEMMA score ≤ 2 had a negative predictive value of 96.3% and 95.7% for identifying lesions with FFR >0.80 and iFR >0.89, respectively. A DILEMMA score ≥ 9 had a positive predictive value of 88.9% and 100% for identifying lesions with FFR ≤0.80 and iFR ≤0.89, respectively. The receiver operating characteristic area under the curve values for DILEMMA score to predict FFR ≤0.80 and iFR ≤0.89 were 0.83 (95% CI 0.77-0.90) and 0.82 (0.75-0.89) respectively. A DILEMMA score ≤ 2 or ≥9 occurred in 172 of the 346 lesions (49.7%).
Conclusions: Using DILEMMA score in patients with coronary stenosis of intermediate severity may reduce the need for pressure wire use, offering potential cost-savings and minimizing the risks associated with invasive physiological lesion assessment.
Keywords: angiography, coronary; coronary artery disease; coronary blood flow/physiology/microvascular function; fractional flow reserve; percutaneous coronary intervention.
© 2019 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
J.E.D. holds patents pertaining to the instantaneous wave-free ratio (iFR) technology. He has served as a consultant for and has received significant research funding from Volcano Corporation. No extramural funding was used to support this analysis.
Figures


References
-
- Beller GA, Zaret BL. Contributions of nuclear cardiology to diagnosis and prognosis of patients with coronary artery disease. Circulation. 2000;101:1465–1478. - PubMed
-
- Tonino PA, Fearon WF, De Bruyne B, et al. Angiographic versus functional severity of coronary artery stenoses in the FAME study fractional flow reserve versus angiography in multivessel evaluation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;55:2816–2821. - PubMed
-
- Fihn SD, Gardin JM, Abrams J, et al. 2012 ACCF/AHA/ACP/AATS/PCNA/SCAI/STS guideline for the diagnosis and management of patients with stable ischemic heart disease: A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association task force on practice guidelines, and the American College of Physicians, American Association for Thoracic Surgery, preventive cardiovascular nurses association, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, and Society of Thoracic Surgeons. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60:e44–e164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

