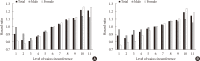The Risk of Myocardial Infarction and Ischemic Stroke According to Waist Circumference in 21,749,261 Korean Adults: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
- PMID: 30604597
- PMCID: PMC6470098
- DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2018.0039
The Risk of Myocardial Infarction and Ischemic Stroke According to Waist Circumference in 21,749,261 Korean Adults: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Abstract
Background: Waist circumference (WC) is a well-known obesity index that predicts cardiovascular disease (CVD). We studied the relationship between baseline WC and development of incident myocardial infarction (MI) and ischemic stroke (IS) using a nationwide population-based cohort, and evaluated if its predictability is better than body mass index (BMI).
Methods: Our study included 21,749,261 Koreans over 20 years of age who underwent the Korean National Health Screening between 2009 and 2012. The occurrence of MI or IS was investigated until the end of 2015 using National Health Insurance Service data.
Results: A total of 127,289 and 181,637 subjects were newly diagnosed with MI and IS. The incidence rate and hazard ratio of MI and IS increased linearly as the WC level increased, regardless of adjustment for BMI. When the analyses were performed according to 11 groups of WC, the lowest risk of MI was found in subjects with WC of 70 to 74.9 and 65 to 69.9 cm in male and female, and the lowest risk of IS in subjects with WC of 65 to 69.9 and 60 to 64.9 cm in male and female, respectively. WC showed a better ability to predict CVD than BMI with smaller Akaike information criterion. The optimal WC cutoffs were 84/78 cm for male/female for predicting MI, and 85/78 cm for male/female for predicting IS.
Conclusion: WC had a significant linear relationship with the risk of MI and IS and the risk began to increase from a WC that was lower than expected.
Keywords: Body mass index; Cardiovascular diseases; Cohort studies; National Health Programs; Observational study; Waist circumference.
Copyright © 2019 Korean Diabetes Association.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Variabilities in Weight and Waist Circumference and Risk of Myocardial Infarction, Stroke, and Mortality: A Nationwide Cohort Study.Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2020 Dec;35(4):933-942. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2020.871. Epub 2020 Dec 23. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2020. PMID: 33397045 Free PMC article.
-
Body mass index, waist circumference and cardiovascular diseases in transitional ages (40 and 66 years).J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2023 Feb;14(1):369-381. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13138. Epub 2022 Dec 15. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2023. PMID: 36522803 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between Body Mass Index, Waist Circumference, and Myocardial Infarction in Older Adults Aged over 75 Years: A Population-Based Cohort Study.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Nov 30;58(12):1768. doi: 10.3390/medicina58121768. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 36556970 Free PMC article.
-
[Myocardial infarction, stroke, and psoriasis: A systematic review of observational studies].Ann Cardiol Angeiol (Paris). 2023 Apr;72(2):101574. doi: 10.1016/j.ancard.2022.11.009. Epub 2022 Dec 16. Ann Cardiol Angeiol (Paris). 2023. PMID: 36529545 French.
-
Recent trends in acute myocardial infarction among the young.Curr Opin Cardiol. 2020 Sep;35(5):524-530. doi: 10.1097/HCO.0000000000000781. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32694263 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Response: The Differential Association between Muscle Strength and Diabetes Mellitus According to the Presence or Absence of Obesity (J Obes Metab Syndr 2019;28:46-52).J Obes Metab Syndr. 2019 Dec;28(4):297-298. doi: 10.7570/jomes.2019.28.4.297. Epub 2019 Dec 30. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2019. PMID: 31909373 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Changes in body composition and subsequent cardiovascular disease risk among 5-year breast cancer survivors.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Nov 20;10:1259292. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1259292. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 38054098 Free PMC article.
-
Letter: Association of Z-Score of the Log-Transformed A Body Shape Index with Cardiovascular Disease in People Who Are Obese but Metabolically Healthy: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007-2010 (J Obes Metab Syndr 2018;27:158-65).J Obes Metab Syndr. 2019 Jun;28(2):139-140. doi: 10.7570/jomes.2019.28.2.139. Epub 2019 Jun 30. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2019. PMID: 31294346 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Multimodal machine learning-based marker enables the link between obesity-related indices and future stroke: a prospective cohort study.EClinicalMedicine. 2025 Jul 1;85:103331. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2025.103331. eCollection 2025 Jul. EClinicalMedicine. 2025. PMID: 40678699 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-differential effect of waist circumference on new-onset cerebral infarction: a nationwide cohort study.Front Neurol. 2024 Oct 9;15:1448428. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1448428. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39445196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Van Gaal LF, Mertens IL, De Block CE. Mechanisms linking obesity with cardiovascular disease. Nature. 2006;444:875–880. - PubMed
-
- Rexrode KM, Carey VJ, Hennekens CH, Walters EE, Colditz GA, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC, Manson JE. Abdominal adiposity and coronary heart disease in women. JAMA. 1998;280:1843–1848. - PubMed
-
- Yusuf S, Hawken S, Ounpuu S, Bautista L, Franzosi MG, Commerford P, Lang CC, Rumboldt Z, Onen CL, Lisheng L, Tanomsup S, Wangai P, Jr, Razak F, Sharma AM, Anand SS INTERHEART Study Investigators. Obesity and the risk of myocardial infarction in 27,000 participants from 52 countries: a case-control study. Lancet. 2005;366:1640–1649. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical