HOXA5 protein expression and genetic fate mapping show lineage restriction in the developing musculoskeletal system
- PMID: 30604848
- PMCID: PMC8783609
- DOI: 10.1387/ijdb.180214jm
HOXA5 protein expression and genetic fate mapping show lineage restriction in the developing musculoskeletal system
Abstract
HOX proteins act during development to regulate musculoskeletal morphology. HOXA5 patterns skeletal structures surrounding the cervical-thoracic transition including the vertebrae, ribs, sternum and forelimb girdle. However, the tissue types in which it acts to pattern the skeleton, and the ultimate fates of embryonic cells that activate Hoxa5 expression are unknown. A detailed characterization of HOXA5 expression by immunofluorescence was combined with Cre/LoxP genetic lineage tracing to map the fate of Hoxa5 expressing cells in axial musculoskeletal tissues and in their precursors, the somites and lateral plate mesoderm. HOXA5 protein expression is dynamic and spatially restricted in derivatives of both the lateral plate mesoderm and somites, including a subset of the lateral sclerotome, suggesting a local role in regulating early skeletal patterning. HOXA5 expression persists from somite stages through late development in differentiating skeletal and connective tissues, pointing to a continuous and direct role in skeletal patterning. In contrast, HOXA5 expression is excluded from the skeletal muscle and muscle satellite cell lineages. Furthermore, the descendants of Hoxa5-expressing cells, even after HOXA5 expression has extinguished, never contribute to these lineages. Together, these findings suggest cell autonomous roles for HOXA5 in skeletal development, as well as non-cell autonomous functions in muscle through expression in surrounding connective tissues. They also support the notion that different Hox genes display diverse tissue specificities and locations to achieve their patterning activity.
Figures


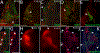
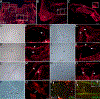


References
-
- ABBOTT MA, JOKSIMOVIC M and TUGGLE CK (2005). Ectopic HOXA5 expression results in abnormal differentiation, migration and p53-independent cell death of superficial dorsal horn neurons. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 159: 87–97. - PubMed
-
- ALVARES LE, SCHUBERT FR, THORPE C, MOOTOOSAMY RC, CHENG L, PARKYN G, LUMSDEN A and DIETRICH S (2003). Intrinsic, Hox-dependent cues determine the fate of skeletal muscle precursors. Dev Cell 5: 379–90. - PubMed
-
- AOYAMA H, MIZUTANI-KOSEKI S and KOSEKI H (2005). Three developmental compartments involved in rib formation. Int J Dev Biol 49: 325–33. - PubMed
-
- AUBIN J, DERY U, LEMIEUX M, CHAILLER P and JEANNOTTE L (2002a). Stomach regional specification requires Hoxa5-driven mesenchymal-epithelial signaling. Development 129: 4075–87. - PubMed
-
- AUBIN J, LEMIEUX M, MOREAU J, LAPOINTE J and JEANNOTTE L (2002b). Cooperation of Hoxa5 and Pax1 genes during formation of the pectoral girdle. Dev Biol 244: 96–113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

