[18F]Amylovis as a Potential PET Probe for β-Amyloid Plaque: Synthesis, In Silico, In vitro and In vivo Evaluations
- PMID: 30605068
- PMCID: PMC6463402
- DOI: 10.2174/1874471012666190102165053
[18F]Amylovis as a Potential PET Probe for β-Amyloid Plaque: Synthesis, In Silico, In vitro and In vivo Evaluations
Abstract
Background: Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia. Neuroimaging methods have widened the horizons for AD diagnosis and therapy. The goals of this work are the synthesis of 2-(3-fluoropropyl)-6-methoxynaphthalene (5) and its [18F]-radiolabeled counterpart ([18F]Amylovis), the in silico and in vitro comparative evaluations of [18F]Amylovis and [11C]Pittsburg compound B (PIB) and the in vivo preclinical evaluation of [18F]Amylovis in transgenic and wild mice.
Methods: Iron-catalysis cross coupling reaction, followed by fluorination and radiofluorination steps were carried out to obtain 5 and 18F-Amylovis. Protein/Aß plaques binding, biodistribution, PET/CT Imaging and immunohistochemical studies were conducted in healthy/transgenic mice.
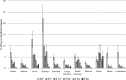
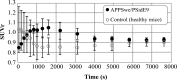
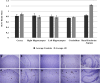
Results: The synthesis of 5 was successful obtained. Comparative in silico studies predicting that 5 should have affinity to the Aβ-peptide, mainly through π-π interactions. According to a dynamic simulation study the ligand-Aβ peptide complexes are stable in simulation-time (ΔG = -5.31 kcal/mol). [18F]Amylovis was obtained with satisfactory yield, high radiochemical purity and specific activity. The [18F]Amylovis log Poct/PBS value suggests its potential ability for crossing the blood brain barrier (BBB). According to in vitro assays, [18F]Amylovis has an adequate stability in time. Higher affinity to Aβ plaques were found for [18F]Amylovis (Kd 0.16 nmol/L) than PIB (Kd 8.86 nmol/L) in brain serial sections of 3xTg-AD mice. Biodistribution in healthy mice showed that [18F]Amylovis crosses the BBB with rapid uptake (7 %ID/g at 5 min) and good washout (0.11±0.03 %ID/g at 60 min). Comparative PET dynamic studies of [18F]Amylovis in healthy and transgenic APPSwe/PS1dE9 mice, revealed a significant high uptake in the mice model.
Conclusion: The in silico, in vitro and in vivo results justify that [18F]Amylovis should be studied as a promissory PET imaging agent to detect the presence of Aβ senile plaques.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease diagnosis; docking and dynamic simulations; fluorine-18; iron cross-coupling reaction; positron emission tomography; β-amyloid probe..
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Longitudinal evaluation of a novel BChE PET tracer as an early in vivo biomarker in the brain of a mouse model for Alzheimer disease.Theranostics. 2021 Apr 26;11(13):6542-6559. doi: 10.7150/thno.54589. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33995675 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and evaluation of a (18)F-curcumin derivate for β-amyloid plaque imaging.Bioorg Med Chem. 2014 May 1;22(9):2753-62. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2014.03.010. Epub 2014 Mar 18. Bioorg Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24702859
-
18F-labeled styrylpyridines as PET agents for amyloid plaque imaging.Nucl Med Biol. 2007 Jan;34(1):89-97. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2006.10.003. Epub 2006 Dec 12. Nucl Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17210465
-
An Exposition of 11C and 18F Radiotracers Synthesis for PET Imaging.Curr Radiopharm. 2021;14(2):92-100. doi: 10.2174/1874471013666201201095631. Curr Radiopharm. 2021. PMID: 33261547 Review.
-
Development of positron emission tomography β-amyloid plaque imaging agents.Semin Nucl Med. 2012 Nov;42(6):423-32. doi: 10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2012.07.001. Semin Nucl Med. 2012. PMID: 23026364 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Medicinal (Radio) Chemistry: Building Radiopharmaceuticals for the Future.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(34):5481-5534. doi: 10.2174/0929867331666230818092634. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37594105 Review.
-
Amylovis-201 is a new dual-target ligand, acting as an anti-amyloidogenic compound and a potent agonist of the σ 1 chaperone protein.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Oct;14(10):4345-4359. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.06.013. Epub 2024 Jun 20. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 39525570 Free PMC article.
-
Ligands for Protein Fibrils of Amyloid-β, α-Synuclein, and Tau.Chem Rev. 2025 Jun 11;125(11):5282-5348. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.4c00838. Epub 2025 May 6. Chem Rev. 2025. PMID: 40327808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuropathological assessment of the Alzheimer spectrum.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2020 Sep;127(9):1229-1256. doi: 10.1007/s00702-020-02232-9. Epub 2020 Aug 1. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2020. PMID: 32740684 Review.
-
The Radioprotective Effect of LBP on Neurogenesis and Cognition after Acute Radiation Exposure.Curr Radiopharm. 2024;17(3):257-265. doi: 10.2174/0118744710274008231220055033. Curr Radiopharm. 2024. PMID: 38204264 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sperling R.A., Aisen P.S., Beckett L.A., Bennett D.A., Craft S., Fagan A.M., Iwatsubo T., Jack C.R., Kaye J., Montine T.J. Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011;7(3):280–292. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Scheuner D., Eckman C., Jensen M., Song X., Citron M., Suzuki N., Bird T., Hardy J., Hutton M., Kukull W. Secreted amyloid β-protein similar to that in the senile plaques of Alzheimer’s disease is increased in vivo by the presenilin 1 and 2 and APP mutations linked to familial Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Med. 1996;2(8):864–870. - PubMed
-
- Monsonego A., Weiner H.L. Immunotherapeutic approaches to Alzheimer’s disease. Science. 2003;302(5646):834–838. - PubMed
-
- DeKosky S.T., Marek K. Looking backward to move forward: Early detection of neurodegenerative disorders. Science. 2003;302(5646):830–834. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

