Statistical Analysis of Nonuniform Volume Distributions for Droplet-Based Digital PCR Assays
- PMID: 30605325
- PMCID: PMC6383768
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.8b09073
Statistical Analysis of Nonuniform Volume Distributions for Droplet-Based Digital PCR Assays
Abstract
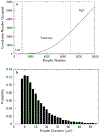
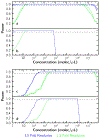
We present a method to determine the concentration of nucleic acids in a sample by partitioning it into droplets with a nonuniform volume distribution. This digital PCR method requires no special equipment for partitioning, unlike other methods that require nearly identical volumes. Droplets are generated by vortexing a sample in an immiscible oil to create an emulsion. PCR is performed, and droplets in the emulsion are imaged. Droplets with one or more copies of a nucleic acid are identified, and the nucleic acid concentration of the sample is determined. Numerical simulations of droplet distributions were used to estimate measurement error and dynamic range and to examine the effects of the total volume of droplets imaged and the shape of the droplet size distribution on measurement accuracy. The ability of the method to resolve 1.5- and 3-fold differences in concentration was assessed by using simulations of statistical power. The method was validated experimentally; droplet shrinkage and fusion during amplification were also assessed experimentally and showed negligible effects on measured concentration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): D.T.C., J.E.K., T.S. and B.S.F. have financial interest in Lamprogen, which has licensed the described technology from the University of Washington.
Figures
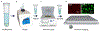
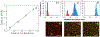
Similar articles
-
Simple Polydisperse Droplet Emulsion Polymerase Chain Reaction with Statistical Volumetric Correction Compared with Microfluidic Droplet Digital Polymerase Chain Reaction.Anal Chem. 2018 Aug 7;90(15):9374-9380. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.8b01988. Epub 2018 Jul 26. Anal Chem. 2018. PMID: 29985594
-
A compact and facile microfluidic droplet creation device using a piezoelectric diaphragm micropump for droplet digital PCR platforms.Electrophoresis. 2017 Oct;38(20):2666-2672. doi: 10.1002/elps.201700039. Epub 2017 Jul 24. Electrophoresis. 2017. PMID: 28657130
-
On-chip, real-time, single-copy polymerase chain reaction in picoliter droplets.Anal Chem. 2007 Nov 15;79(22):8471-5. doi: 10.1021/ac701809w. Epub 2007 Oct 11. Anal Chem. 2007. PMID: 17929880
-
Single-molecule emulsion PCR in microfluidic droplets.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012 Jun;403(8):2127-43. doi: 10.1007/s00216-012-5914-x. Epub 2012 Mar 27. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012. PMID: 22451171 Review.
-
Digital Assays Part I: Partitioning Statistics and Digital PCR.SLAS Technol. 2017 Aug;22(4):369-386. doi: 10.1177/2472630317705680. Epub 2017 Apr 27. SLAS Technol. 2017. PMID: 28448765 Review.
Cited by
-
Deep-dLAMP: Deep Learning-Enabled Polydisperse Emulsion-Based Digital Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022 Mar;9(9):e2105450. doi: 10.1002/advs.202105450. Epub 2022 Jan 24. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022. PMID: 35072353 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of multiple displacement amplification for metagenomic analysis of low biomass samples.ISME Commun. 2024 Feb 12;4(1):ycae024. doi: 10.1093/ismeco/ycae024. eCollection 2024 Jan. ISME Commun. 2024. PMID: 38500705 Free PMC article.
-
One-Tube Nested PCR Coupled with CRISPR-Cas12a for Ultrasensitive Nucleic Acid Testing.ACS Omega. 2024 Sep 13;9(38):39616-39625. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c03911. eCollection 2024 Sep 24. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39346871 Free PMC article.
-
Near-digital amplification in paper improves sensitivity and speed in biplexed reactions.Sci Rep. 2022 Aug 26;12(1):14618. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-18937-8. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36028745 Free PMC article.
-
A critical review: Recent advances in "digital" biomolecule detection with single copy sensitivity.Biosens Bioelectron. 2021 Apr 1;177:112901. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112901. Epub 2021 Jan 4. Biosens Bioelectron. 2021. PMID: 33472132 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Saunders CJ; Miller NA; Soden SE; Dinwiddie DL; Noll A; Alnadi NA; Andraws N; Patterson ML; Krivohlavek LA; Fellis J; Humphray S; Saffrey P; Kingsbury Z; Weir JC; Betley J; Grocock RJ; Margulies EH; Farrow EG; Artman M; Safina NP; Petrikin JE; Hall KP; Kingsmore SF Rapid Whole-Genome Sequencing for Genetic Disease Diagnosis in Neonatal Intensive Care Units. Sci Transl Med 2012, 4, 154ra135. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Worthey EA; Mayer AN; Syverson GD; Helbling D; Bonacci BB; Decker B; Serpe JM; Dasu T; Tschannen MR; Veith RL; Basehore MJ; Broeckel U; Tomita-Mitchell A; Arca MJ; Casper JT; Margolis DA; Bick DP; Hessner MJ; Routes JM; Verbsky JW; Jacob HJ; Dimmock DP Making a definitive diagnosis: Successful clinical application of whole exome sequencing in a child with intractable inflammatory bowel disease. Genet. Med 2011, 13, 255. - PubMed
-
- Gyan E; Frew M; Bowen D; Beldjord C; Preudhomme C; Lacombe C; Mayeux P; Dreyfus F; Porteu F; Fontenay M Mutation in RAP1 is a rare event in myelodysplastic syndromes. Leukemia 2005, 19, 1678. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

