Optically Responsive, Smart Anti-Bacterial Coatings via the Photofluidization of Azobenzenes
- PMID: 30605328
- PMCID: PMC6552654
- DOI: 10.1021/acsami.8b21058
Optically Responsive, Smart Anti-Bacterial Coatings via the Photofluidization of Azobenzenes
Abstract
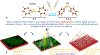
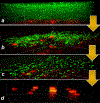
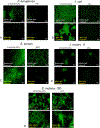
Antibacterial strategies sans antibiotic drugs have recently garnered much interest as a mechanism by which to inhibit biofilm formation and growth on surfaces due to the rise of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Based on the photofluidization of azobenzenes, we demonstrate for the first time the ability achieve up to a 4 log reduction in bacterial biofilms by opto-mechanically activating the disruption and dispersion of biofilms. This unique strategy with which to enable biofilm removal offers a novel paradigm with which to combat antibiotic resistance.
Keywords: antibacterial and antifouling strategies; antibacterial coatings; azobenzenes; optically responsive materials; photofluidization; photoresponsive polymers; smart materials.
Figures

References
-
- Bao Q; Nishimura N; Kamata H; Furue K; Ono Y; Hosomi M; Terada A Antibacterial and Anti-Biofilm Efficacy of Fluoropolymer Coating by a 2,3,5,6-Tetrafluoro-p-Phenylenedimethanol Structure. Colloids Surf. B 2017, 151, 363–371. - PubMed
-
- Gilbert P; Allison DG; McBain AJ Biofilms in Vitro and in Vivo: Do Singular Mechanisms Imply Cross-Resistance? J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 92 (s1), 98S–110S. - PubMed
-
- O’Neill J Tackling Drug-Resistant Infections Globally: Final Report and Recommendations. Rev. Antimicrob. Resist. 2016, May, 1–75.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

