Magnesium controls aptamer-expression platform switching in the SAM-I riboswitch
- PMID: 30605518
- PMCID: PMC6451092
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gky1311
Magnesium controls aptamer-expression platform switching in the SAM-I riboswitch
Abstract
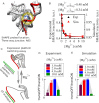
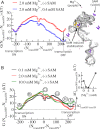
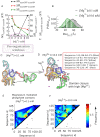
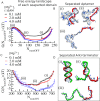
Investigations of most riboswitches remain confined to the ligand-binding aptamer domain. However, during the riboswitch mediated transcription regulation process, the aptamer domain and the expression platform compete for a shared strand. If the expression platform dominates, an anti-terminator helix is formed, and the transcription process is active (ON state). When the aptamer dominates, transcription is terminated (OFF state). Here, we use an expression platform switching experimental assay and structure-based electrostatic simulations to investigate this ON-OFF transition of the full length SAM-I riboswitch and its magnesium concentration dependence. Interestingly, we find the ratio of the OFF population to the ON population to vary non-monotonically as magnesium concentration increases. Upon addition of magnesium, the aptamer domain pre-organizes, populating the OFF state, but only up to an intermediate magnesium concentration level. Higher magnesium concentration preferentially stabilizes the anti-terminator helix, populating the ON state, relatively destabilizing the OFF state. Magnesium mediated aptamer-expression platform domain closure explains this relative destabilization of the OFF state at higher magnesium concentration. Our study reveals the functional potential of magnesium in controlling transcription of its downstream genes and underscores the importance of a narrow concentration regime near the physiological magnesium concentration ranges, striking a balance between the OFF and ON states in bacterial gene regulation.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research 2019.
Figures


References
-
- Grundy F.J., Henkin T.M.. The S box regulon: a new global transcription termination control system for methionine and cysteine biosynthesis genes in gram-positive bacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 1998; 30:737–749. - PubMed
-
- Montange R.K., Batey R.T.. Riboswitches: emerging themes in RNA structure and function. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2008; 37:117–133. - PubMed
-
- Nahvi A., Sudarsan N., Ebert M.S., Zou X., Brown K.L., Breaker R.R.. Genetic control by a metabolite binding mRNA. Chem. Biol. 2002; 9:1043. - PubMed
-
- Batey R.T. Structures of regulatory elements in mRNAs. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2006; 16:299–306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

