Natural Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Ligands: Biosynthesis and Biology
- PMID: 30605564
- PMCID: PMC6579537
- DOI: 10.1002/cbic.201800754
Natural Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Ligands: Biosynthesis and Biology
Abstract
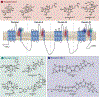
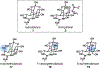
Natural product biosynthetic pathways are composed of enzymes that use powerful chemistry to assemble complex molecules. Small molecule neurotoxins are examples of natural products with intricate scaffolds which often have high affinities for their biological targets. The focus of this Minireview is small molecule neurotoxins targeting voltage-gated sodium channels (VGSCs) and the state of knowledge on their associated biosynthetic pathways. There are three small molecule neurotoxin receptor sites on VGSCs associated with three different classes of molecules: guanidinium toxins, alkaloid toxins, and ladder polyethers. Each of these types of toxins have unique structural features which are assembled by biosynthetic enzymes and the extent of information known about these enzymes varies among each class. The biosynthetic enzymes involved in the formation of these toxins have the potential to become useful tools in the efficient synthesis of VGSC probes.
Keywords: biocatalysis; biosynthesis; enzymes; neurotoxins; voltage-gated sodium channels.
© 2019 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures



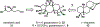
Similar articles
-
The insecticidal neurotoxin Aps III is an atypical knottin peptide that potently blocks insect voltage-gated sodium channels.Biochem Pharmacol. 2013 May 15;85(10):1542-54. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.02.030. Epub 2013 Mar 6. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23473802 Free PMC article.
-
Guanidinium Toxins and Their Interactions with Voltage-Gated Sodium Ion Channels.Mar Drugs. 2017 Oct 13;15(10):303. doi: 10.3390/md15100303. Mar Drugs. 2017. PMID: 29027912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
C2-Modified Sparteine Derivatives Are a New Class of Potentially Long-Acting Sodium Channel Blockers.ChemMedChem. 2017 Nov 22;12(22):1819-1822. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201700568. Epub 2017 Nov 6. ChemMedChem. 2017. PMID: 29045055
-
Exploring the obscure profiles of pharmacological binding sites on voltage-gated sodium channels by BmK neurotoxins.Protein Cell. 2011 Jun;2(6):437-44. doi: 10.1007/s13238-011-1064-8. Epub 2011 Jul 12. Protein Cell. 2011. PMID: 21748593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insect-selective spider toxins targeting voltage-gated sodium channels.Toxicon. 2007 Mar 15;49(4):490-512. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2006.11.027. Epub 2006 Dec 5. Toxicon. 2007. PMID: 17223149 Review.
Cited by
-
Spider Knottin Pharmacology at Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels and Their Potential to Modulate Pain Pathways.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Oct 29;11(11):626. doi: 10.3390/toxins11110626. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31671792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of chemical defense in harlequin toads (Bufonidae: Atelopus).Toxicon X. 2022 Jan 22;13:100092. doi: 10.1016/j.toxcx.2022.100092. eCollection 2022 Mar. Toxicon X. 2022. PMID: 35146414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Linking Genes to Molecules in Eukaryotic Sources: An Endeavor to Expand Our Biosynthetic Repertoire.Molecules. 2020 Jan 31;25(3):625. doi: 10.3390/molecules25030625. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32023950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Grayanane Diterpenes: Isolation, Structural Diversity, and Bioactivities from Ericaceae Family (2018-2024).Molecules. 2024 Apr 6;29(7):1649. doi: 10.3390/molecules29071649. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38611928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential effects of modified batrachotoxins on voltage-gated sodium channel fast and slow inactivation.Cell Chem Biol. 2022 Apr 21;29(4):615-624.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2021.12.003. Epub 2021 Dec 27. Cell Chem Biol. 2022. PMID: 34963066 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

