Site-specific effects of aromatase inhibition on the activation of male sexual behavior in male Japanese quail (Coturnix japonica)
- PMID: 30605622
- PMCID: PMC6377315
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2018.12.015
Site-specific effects of aromatase inhibition on the activation of male sexual behavior in male Japanese quail (Coturnix japonica)
Abstract
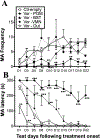
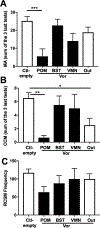
Aromatization within the medial preoptic nucleus (POM) is essential for the expression of male copulatory behavior in Japanese quail. However, several nuclei within the social behavior network (SBN) also express aromatase. Whether aromatase in these loci participates in the behavioral activation is not known. Castrated male Japanese quail were implanted with 2 subcutaneous Silastic capsules filled with crystalline testosterone and with bilateral stereotaxic implants filled with the aromatase inhibitor Vorozole targeting the POM, the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BST) or the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus (VMN). Control animals were implanted with testosterone and empty bilateral stereotaxic implants. Starting 2 days after the surgery, subjects were tested for the expression of consummatory sexual behavior (CSB) every other day for a total of 10 tests. They were also tested once for appetitive sexual behavior (ASB) as measured by the rhythmic cloacal sphincter movements displayed in response to the visual presentation of a female. CSB was drastically reduced when the Vorozole implants were localized in the POM, but not in the BST nor in the VMN. Birds with implants in the BST took longer to show CSB in the first 6 tests than controls, suggesting a role of the BST in the acquisition of the full copulatory ability. ASB was not significantly affected by aromatase blockade in any region. These data confirm the key role played by the POM in the control of male sexual behavior and suggest a minor role for aromatization in the BST or VMN.
Keywords: Bed nucleus of the stria terminalis; Bird; Consummatory sexual behavior; Medial preoptic area; Neuroestrogens.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Adkins-Regan EK, 2012. Hormonal organization and activation: Evolutionary implications and questions. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol 176, 279–285. - PubMed
-
- Adkins EK, 1977. Effects of diverse androgens on the sexual behavior and morphology of castrated male quail. Horm. Behav 8, 201–7. - PubMed
-
- Adkins EK, Adler NT, 1972. Hormonal control of behavior in the Japanese quail. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol 81, 27–36. - PubMed
-
- Adkins EK, Boop JJ, Koutnik DL, Morris JB, Pniewski EE, 1980. Further evidence that androgen aromatization is essential for the activation of copulation in male quail. Physiol. Behav 24, 441–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

