The anti-obesity effects of Tongbi-san in a high-fat diet-induced obese mouse model
- PMID: 30606178
- PMCID: PMC6319014
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-018-2420-5
The anti-obesity effects of Tongbi-san in a high-fat diet-induced obese mouse model
Abstract
Background: Recently, it has been noted that natural herbal medications may be effective in treating obesity. Tongbi-san (TBS) is a traditional medicine usually used for dysuria (i.e., painful urination), containing three herbs, Cyperus rotundus L., Citrus unshiu Markovich, and Poria cocos. In this study, we aimed to examine whether TBS can inhibit high-fat diet (HFD)-induced adipogenesis in the liver and epididymal adipose tissue of obese mice.
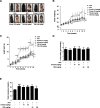
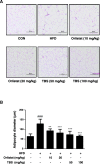
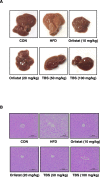
Methods: Male C57BL/6 N mice were fed a normal diet, an HFD, an HFD plus orlistat 10 or 20 mg/kg, or an HFD plus TBS 50 or 100 mg/kg for 11 weeks. Body weight was checked weekly and histological tissue examinations were investigated. An expression of genes involved in adipogenesis was also assessed.
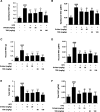
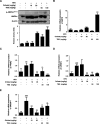
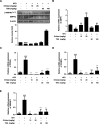
Results: Oral administration of TBS significantly reduced body weight and decreased epididymal and visceral white adipose tissue (WAT) weight. In addition, we found that TBS enhanced the expression of the adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and inhibited the expression of transcription factors, such as CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins (C/EBPs), sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP1), and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) in the liver and epididymal WAT as measured by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR).
Conclusion: These findings demonstrate that the anti-obesity effects of TBS may be linked to the activation of AMPK.
Keywords: AMPK; Adipogenesis; High-fat diet; Obesity; Tongbi-san.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All procedures were conducted in accordance with the National Institute of Health guidelines and approved by the Ethical Committee for Animal Care and the Use of Laboratory Animal of Sangji University (reg.no. 2017–12).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Zou T, Wang B, Yang Q, de Avila JM, Zhu MJ, You J, Chen D, Du M. Raspberry promotes brown and beige adipocyte development in mice fed high-fat diet through activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) alpha1. J Nutr Biochem. 2018;55:157–164. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.02.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

