Linking Duplication of a Calcium Sensor to Salt Tolerance in Eutrema salsugineum
- PMID: 30606887
- PMCID: PMC6393783
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.18.01400
Linking Duplication of a Calcium Sensor to Salt Tolerance in Eutrema salsugineum
Abstract
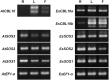
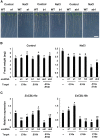
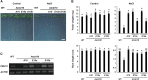
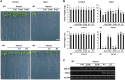
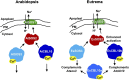
The SALT-OVERLY-SENSITIVE (SOS) pathway in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) functions to prevent the toxic accumulation of sodium in the cytosol when plants are grown in salt-affected soils. In this pathway, the CALCINEURIN B-LIKE10 (AtCBL10) calcium sensor interacts with the AtSOS2 kinase to activate the AtSOS1 plasma membrane sodium/proton exchanger. CBL10 has been duplicated in Eutrema (Eutrema salsugineum), a salt-tolerant relative of Arabidopsis. Because Eutrema maintains growth in salt-affected soils that kill most crop plants, the duplication of CBL10 provides a unique opportunity to functionally test the outcome of gene duplication and its link to plant salt tolerance. In Eutrema, individual down-regulation of the duplicated CBL10 genes (EsCBL10a and EsCBL10b) decreased growth in the presence of salt and, in combination, led to an even greater decrease, suggesting that both genes function in response to salt and have distinct functions. Cross-species complementation assays demonstrated that EsCBL10b has an enhanced ability to activate the SOS pathway while EsCBL10a has a function not performed by AtCBL10 or EsCBL10b Chimeric EsCBL10a/EsCBL10b proteins revealed that the specific functions of the EsCBL10 proteins resulted from changes in the amino terminus. The duplication of CBL10 increased calcium-mediated signaling capacity in Eutrema and conferred increased salt tolerance to salt-sensitive Arabidopsis.
© 2019 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures



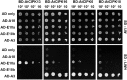
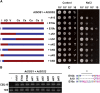
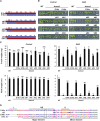
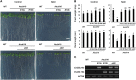
Similar articles
-
Duplication and functional divergence of a calcium sensor in the Brassicaceae.J Exp Bot. 2020 May 9;71(9):2782-2795. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eraa031. J Exp Bot. 2020. PMID: 31989164 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Arabidopsis thaliana HKT1 and Eutrema salsugineum/botschantzevii HKT1;2 Promoters in Response to Salt Stress in Athkt1:1 Mutant.Mol Biotechnol. 2019 Jun;61(6):442-450. doi: 10.1007/s12033-019-00175-5. Mol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30980224
-
Distinct roles for SOS1 in the convergent evolution of salt tolerance in Eutrema salsugineum and Schrenkiella parvula.Mol Biol Evol. 2014 Aug;31(8):2094-107. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msu152. Epub 2014 May 6. Mol Biol Evol. 2014. PMID: 24803640
-
Halophytism: What Have We Learnt From Arabidopsis thaliana Relative Model Systems?Plant Physiol. 2018 Nov;178(3):972-988. doi: 10.1104/pp.18.00863. Epub 2018 Sep 20. Plant Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30237204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural Variation in Freezing Tolerance and Cold Acclimation Response in Arabidopsis thaliana and Related Species.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1081:81-98. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-1244-1_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 30288705 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrating differential expression under drought with gene family expansion unique to drought-tolerant species prioritizes candidate genes for drought adaptation in Brassicaceae species.BMC Genomics. 2025 Jun 19;26(1):571. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11737-0. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40537742 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium signaling and salt tolerance are diversely entwined in plants.Plant Signal Behav. 2019;14(11):1665455. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2019.1665455. Epub 2019 Sep 28. Plant Signal Behav. 2019. PMID: 31564206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Haplotype-resolved genome of Mimosa bimucronata revealed insights into leaf movement and nitrogen fixation.BMC Genomics. 2024 Apr 3;25(1):334. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10264-8. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38570736 Free PMC article.
-
Eutrema EsMYB90 Gene Improves Growth and Antioxidant Capacity of Transgenic Wheat Under Salinity Stress.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Apr 29;13:856163. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.856163. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35574106 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis of upland cotton revealed novel pathways to scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS) responding to Na2SO4 tolerance.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 21;11(1):8670. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87999-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33883626 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akaboshi M, Hashimoto H, Ishida H, Saijo S, Koizumi N, Sato M, Shimizu T (2008) The crystal structure of plant-specific calcium-binding protein AtCBL2 in complex with the regulatory domain of AtCIPK14. J Mol Biol 377: 246–257 - PubMed
-
- Amarasinghe S, Watson-Haigh NS, Gilliham M, Roy S, Baumann U (2016) The evolutionary origin of CIPK16: A gene involved in enhanced salt tolerance. Mol Phylogenet Evol 100: 135–147 - PubMed
-
- Bartlett MS. (1937) Properties of sufficiency and statistical tests. Proc R Soc Lond A Math Phys Sci 160: 268–282
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

