Factors Influencing Prescribing Decisions of Physicians: A Review
- PMID: 30607097
- PMCID: PMC6308758
- DOI: 10.4314/ejhs.v28i6.15
Factors Influencing Prescribing Decisions of Physicians: A Review
Abstract
Background: The pharmaceutical bill is increasing at an alarming rate. The physician practice variation has a pronounced effect on healthcare spending. A number of factors can influence the prescribing behavior of physicians. The aim of this review was to identify the factors affecting the prescribing decision of physicians.
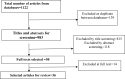
Methods: Electronic databases including Scopus, PubMed/MEDLINE CENTRAL, Cochrane Libraries and Google scholar were searched systematically for literatures on factors influencing prescribing decisions of physicians from 2000 to 2016. There was no restriction on the study designs.
Results: Thirty-three studies met the inclusion criteria from 1122 search results. A total of 33 factors were identified. The most frequent factors were patients' clinical condition, pharmaceutical industries, physician attributes, patient preference and cost of medicine.
Conclusion: Physicians' personal attributes, cost of the medicine and pharmaceutical industries' marketing and promotion strategies were mostly mentioned to influence prescribing decision. The identified factors showed that prescribing is not only geared for patient benefit, but also towards personal interest. The use of valid and reliable practice guidelines could reduce the negative impact of wide ranges of factors and promote the rational prescribing effectively.
Keywords: guideline; physician; prescribing behavior; prescribing decision; systematic review.
Figures
References
-
- Lu Y, Hernandez P, Abegunde D, Edejer T. The world medicines situation 2011. Medicine expenditures. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2011.
-
- OECD, author. Health at a Glance 2011. OECD Indicators. Vol. 15. Paris: OECD Publishing; 2016. [February. 2015]. DOI: https://doi.org/101787/health_glance-2015-en.
-
- Ali S, Chambers A, Johnson DW, Newton AS, Vandermeer B, Williamson J, et al. Reported practice variation in pediatric pain management: a survey of Canadian pediatric emergency physicians. Canadian Journal of Emergency Medicine. 2014;16(5):352–360. - PubMed
-
- Blumenthal D, Stremikis K, Cutler D. Health care spending—a giant slain or sleeping? n engl j med. 2013;396(26):2551–2557. - PubMed
-
- Hossain M, Kawsar S, Tanmy T. Assessment of influencing factors on prescription practices of physicians in Bangladesh. Int Res J Pharm. 2013;4
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous