Reducing postsurgical exudate in breast cancer patients by using San Huang decoction to ameliorate inflammatory status: a prospective clinical trial
- PMID: 30607117
- PMCID: PMC6291285
- DOI: 10.3747/co.25.4108
Reducing postsurgical exudate in breast cancer patients by using San Huang decoction to ameliorate inflammatory status: a prospective clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Reducing inflammatory factors in wound exudate is a promising treatment approach for healing wounds in postsurgical breast cancer patients. Traditional Chinese Medicine (tcm) treatments have been shown to be beneficial and safe for optimal regulation of oxidative stress during the postoperative period. In the present clinical trial, we evaluated the effectiveness of a promising Chinese herbal formula, San Huang decoction [shd (Radix astragali, Radix et rhizoma rhei, and Rhizoma curcuma longa, 3:1:1; supplemental Table 1)], on wound inflammatory response after mastectomy.
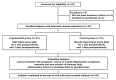
Methods: The study randomized 30 patients with breast cancer who fulfilled the inclusion and exclusion criteria to either a treatment (n = 15) or a control group (n = 15). Patients in the treatment group received liquid shd, taken twice daily with or without food. Treatment was given for 1 day before surgery and for 7 days postoperatively. Participants in the control group received a placebo on the same schedule as the treatment group. Outcomes measured in every subject included clinical tcm and wound inflammation symptom scores, daily and total amounts of drainage fluid, and levels of inflammatory factors in the exudate [tumour necrosis factor α (tnf-α), interleukins 6 (il-6), 8 (il-8), and 2R (il-2R), human C-reactive protein (crp)] at 2 hours and on days 1, 3, and 7 postoperatively.
Results: The total amount of drainage fluid over 7 days was significantly lower in the treatment group (572.20 ± 93.95 mL) than in the control group (700.40 ± 107.38 mL). The tcm symptom score was also lower in treatment group (day 7: 1.87 ± 0.83 vs. 4.80 ± 3.61, p = 0.049), as was the inflammatory symptom score (day 7: 0.67 ± 0.72 vs. 3.67 ± 2.50, p = 0.001). Levels of tnf-α, il-6, il-8, il-2R, and crp in drainage fluid were significantly lower with shd treatment.
Conclusions: Perioperative treatment with shd effectively lessened postoperative exudate and ameliorated inflammatory symptoms in patients who underwent surgery for breast cancer.
Keywords: Breast cancer surgery; San Huang decoction; Traditional Chinese Medicine; complementary medicine; exudate; flaps; inflammation; inflammatory factors; tcm.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST DISCLOSURES We have read and understood Current Oncology’s policy on disclosing conflicts of interest, and we declare that we have none.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antistress Effects of San-Huang-Xie-Xin Decoction on Restraint-Stressed Mice Revealed by 1H NMR-Based Metabolomics and Biochemistry Analysis.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Apr 16;2019:5897675. doi: 10.1155/2019/5897675. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31178969 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the Chinese herbal medicine Hong Huang decoction, on myocardial injury in breast cancer patients who underwent anthracycline-based chemotherapy.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Jul 22;9:921753. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.921753. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35935647 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the clinical efficacy and TCM syndrome element changes of modified Longgu Muli Decoction in the treatment of chronic atrophic gastritis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Apr 4;104(14):e41828. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041828. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40193683 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes is an inflammatory disease: evidence from traditional Chinese medicines.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011 Apr;13(4):289-301. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2010.01336.x. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011. PMID: 21205111 Review.
-
Erxian decoction, a Chinese herbal formula, for menopausal syndrome: An updated systematic review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Apr 24;234:8-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.01.010. Epub 2019 Jan 15. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30658181
Cited by
-
Chinese herbal compound SanHuang decoction reverses axitinib resistance in ccRCC through regulating immune cell infiltration by affecting ADAMTS18 expression.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 Jul 15;13(7):2841-2860. eCollection 2023. Am J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37560000 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical trial-identified inflammatory biomarkers in breast and pancreatic cancers.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Apr 27;14:1106520. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1106520. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37181043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sanhuang Decoction Controls Tumor Microenvironment by Ameliorating Chronic Stress in Breast Cancer: A Report of Ninety Cases.Front Oncol. 2021 Aug 17;11:677939. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.677939. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34485118 Free PMC article.
-
Sophoridine inhibits proliferation and migration by targeting PIM1 in breast cancer.Pharm Biol. 2025 Dec;63(1):503-523. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2025.2537123. Epub 2025 Jul 24. Pharm Biol. 2025. PMID: 40708207 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Turmeric and Curcumin in Prevention and Treatment of Chronic Diseases: Lessons Learned from Clinical Trials.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2023 Mar 6;6(4):447-518. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.2c00012. eCollection 2023 Apr 14. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2023. PMID: 37082752 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous