Speckle-type POZ protein functions as a tumor suppressor in non-small cell lung cancer due to DNA methylation
- PMID: 30607139
- PMCID: PMC6304003
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-018-0711-z
Speckle-type POZ protein functions as a tumor suppressor in non-small cell lung cancer due to DNA methylation
Abstract
Background: Tumor suppressor epigenetic silencing plays an important role in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) development and progression. Previously, the expression of speckle-type POZ protein (SPOP) has been found to be significantly inhibited in NSCLC. Our research aimed to investigate the molecular mechanisms, clinical significance and epigenetic alteration of SPOP in NSCLC.
Materials and methods: Bisulfite sequencing PCR and methylation-specific PCR were performed to test gene methylation. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) was performed to detect transcription factor C/EBPα combinations and the promoter of the SPOP gene. Furthermore, we evaluated the effects of C/EBPα siRNA on SPOP expression, tumor cell migration and proliferation via MTT and Transwell assays in vitro and tumor growth in vivo. The relationship between the methylation status of the SPOP gene and clinicopathologic characteristics was investigated.
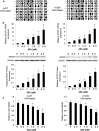
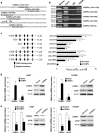
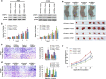
Results: Hypermethylation was found in the CpG island of the SPOP gene promoter in NSCLC tissues, and this methylation was found to be correlated with SPOP expression. SPOP promoter methylation was associated with the pathology grade. The transcriptional activities were significantly inhibited by the hypermethylation of specific CpG sites within the SPOP gene promoter, while 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine significantly increased SPOP gene expression. C/EBPα also played a key role in SPOP regulation. Five C/EBPα binding sites in the CpG island of the SPOP gene promoter were identified by ChIP. Inhibition of C/EBPα significantly reduced SPOP expression. SPOP mediated the C/EBPα-regulated suppression of invasion, migration and proliferation in vitro and tumor growth in vivo.
Conclusions: SPOP function and expression in NSCLS were regulated by DNA methylation and C/EBPα transcriptional regulation combination effects, indicating that the SPOP promoter methylation status could be utilized as an epigenetic biomarker and that the C/EBPα-SPOP signaling pathway could be a potential therapeutic target in NSCLC.
Keywords: C/EBPα; DNA methylation; NSCLC; SPOP; Transcriptional regulation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hypermethylation of the G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6 (GRK6) promoter inhibits binding of C/EBPα, and GRK6 knockdown promotes cell migration and invasion in lung adenocarcinoma cells.FEBS Open Bio. 2019 Mar 19;9(4):605-617. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12606. eCollection 2019 Apr. FEBS Open Bio. 2019. PMID: 30984536 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing speckle-type POZ protein by promoter hypermethylation decreases cell apoptosis through upregulating Hedgehog signaling pathway in colorectal cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2016 Dec 29;7(12):e2569. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.435. Cell Death Dis. 2016. PMID: 28032859 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic modulation of tumor suppressor CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha activity in lung cancer.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006 Mar 15;98(6):396-406. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djj093. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006. PMID: 16537832
-
Clinical significance of SPOP and APC gene alterations in colorectal cancer in Indian population.Mol Genet Genomics. 2023 Sep;298(5):1087-1105. doi: 10.1007/s00438-023-02029-x. Epub 2023 Jun 8. Mol Genet Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37289229
-
Functional roles of Speckle-Type Poz (SPOP) Protein in Genomic stability.J Cancer. 2018 Sep 7;9(18):3257-3262. doi: 10.7150/jca.25930. eCollection 2018. J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30271484 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hypermethylation of the G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6 (GRK6) promoter inhibits binding of C/EBPα, and GRK6 knockdown promotes cell migration and invasion in lung adenocarcinoma cells.FEBS Open Bio. 2019 Mar 19;9(4):605-617. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12606. eCollection 2019 Apr. FEBS Open Bio. 2019. PMID: 30984536 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges and opportunities for the diverse substrates of SPOP E3 ubiquitin ligase in cancer.Theranostics. 2025 May 8;15(13):6111-6145. doi: 10.7150/thno.113356. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 40521202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decreased expression of SLC16A12 mRNA predicts poor prognosis of patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Jul;98(30):e16624. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016624. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31348313 Free PMC article.
-
SPOP and cancer: a systematic review.Am J Cancer Res. 2020 Mar 1;10(3):704-726. eCollection 2020. Am J Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32266086 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SPOP downregulation promotes bladder cancer progression based on cancer cell-macrophage crosstalk via STAT3/CCL2/IL-6 axis and is regulated by VEZF1.Theranostics. 2024 Oct 7;14(17):6543-6559. doi: 10.7150/thno.101575. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 39479456 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

