Exploring the interaction between epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase and some of the synthesized inhibitors using combination of in-silico and in-vitro cytotoxicity methods
- PMID: 30607149
- PMCID: PMC6288988
- DOI: 10.4103/1735-5362.245963
Exploring the interaction between epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase and some of the synthesized inhibitors using combination of in-silico and in-vitro cytotoxicity methods
Abstract
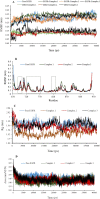
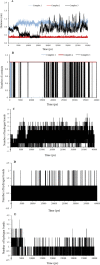
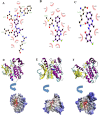
Quinazoline derivatives are potent inhibitors of human epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) as anticancer agents. In this study, the cytotoxic effects of a new series of synthesized quinazoline derivatives were evaluated using MTT assay against MCF-7 and HT-29 cell lines. Using molecular docking, the binding modes of all compounds were analyzed at the binding site of EGFR. Based on the results, the compounds L1, L2, L4, L5, L6, L7, L10, L15, and L18 may be promising EGFR inhibitors based on docking score and hydrogen bonds. Consistent with the experimental data, Met769 is recognized as a key residue in the binding of potential inhibitors. According to the MTT cytotoxicity assays, Lipinski's rule of five (RO5), absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity (ADMET) parameters, and docking studies, three compounds L4, L15, and L10 with IC50 values of 80, 60, and 1 μM against the MCF-7 were selected for further comparative assessments. The dynamics of free EGFR, and selected ligand-EGFR complexes were investigated using molecular dynamics (MD) simulation studies. The results indicated that the three compounds bound to EGFR active site in a stable manner during the simulation through the formation of new hydrogen bonds with Phe699, Leu694, Gly700, Lys721, Met769, Arg817, and Asp831 with the superiority of compound L15. These features can promote future drug candidate designing to produce better derivatives in the search for the anticancer agents.
Keywords: 4(3H)-quinazolinones; 4-Anilinoquinazoline; EGFR; Molecular docking; Molecular dynamics simulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synthesis, Molecular Dynamics Simulation, and In-vitro Antitumor Activity of Quinazoline-2,4,6-triamine Derivatives as Novel EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors.Iran J Pharm Res. 2023 Jan 29;21(1):e133840. doi: 10.5812/ijpr-133840. eCollection 2022 Dec. Iran J Pharm Res. 2023. PMID: 36915409 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of novel JAK2 and EGFR inhibitors from a series of thiazole-based chalcone derivatives.RSC Med Chem. 2021 Feb 26;12(3):430-438. doi: 10.1039/d0md00436g. eCollection 2021 Mar 1. RSC Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34046625 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, characterization, screening and docking analysis of 4-anilinoquinazoline derivatives as tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Eur J Med Chem. 2013 Mar;61:84-94. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2012.07.036. Epub 2012 Jul 27. Eur J Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 22867529
-
Computational Studies of bis-2-Oxoindoline Succinohydrazides and their In Vitro Cytotoxicity.Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2020;16(3):270-280. doi: 10.2174/1573409915666190117122139. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2020. PMID: 30652647
-
Novel ruthenium complexes ligated with 4-anilinoquinazoline derivatives: synthesis, characterisation and preliminary evaluation of biological activity.Eur J Med Chem. 2014 Apr 22;77:110-20. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.02.062. Epub 2014 Mar 1. Eur J Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24631730
Cited by
-
Comparative differential cytotoxicity of clinically used SERMs in human cancer lines of different origin and its predictive molecular docking studies of key target genes involved in cancer progression and treatment responses.Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2021 Dec 31;3:100080. doi: 10.1016/j.crphar.2021.100080. eCollection 2022. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2021. PMID: 35059624 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinspired thiazolo-[2,3-b] quinazolin-6-one derivatives as potent anti-cancer agents targeting EGFR: their biological evaluations and in silico assessment.Mol Divers. 2024 Aug;28(4):2479-2494. doi: 10.1007/s11030-023-10688-6. Epub 2023 Jul 3. Mol Divers. 2024. PMID: 37395840
-
Computational Approaches in Preclinical Studies on Drug Discovery and Development.Front Chem. 2020 Sep 11;8:726. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2020.00726. eCollection 2020. Front Chem. 2020. PMID: 33062633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational Prediction of Resistance Induced Alanine-Mutation in ATP Site of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 13;23(24):15828. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415828. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555475 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of mutation on neurotoxicity reduction of new chimeric reteplase, a computational study.Res Pharm Sci. 2023 Jun 1;18(4):404-412. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.378087. eCollection 2023 Jul-Aug. Res Pharm Sci. 2023. PMID: 37614611 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xu H, Yu Y, Marciniak D, Rishi AK, Sarkar FH, Kucuk O, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-related protein inhibits multiple members of the EGFR family in colon and breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005;4(3):435–342. - PubMed
-
- Ismail RS, Ismail NS, Abuserii S, El Ella DAA. Recent advances in 4-aminoquinazoline based scaffold derivatives targeting EGFR kinases as anticancer agents. Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2016;2(1):9–19.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
