Effects of thyroid-stimulating hormone on adhesion molecules and pro-inflammatory cytokines secretion in human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- PMID: 30607152
- PMCID: PMC6288987
- DOI: 10.4103/1735-5362.245966
Effects of thyroid-stimulating hormone on adhesion molecules and pro-inflammatory cytokines secretion in human umbilical vein endothelial cells
Abstract
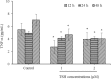
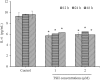
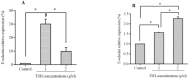
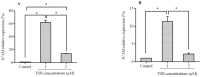
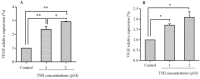
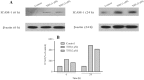
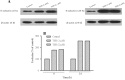
Atherosclerosis is a multifactorial disorder, which affects the arterial wall. It has been reported that, hypothyroidism and thyroid hormone deficiency are related to cardiovascular disorders. Also, endothelial dysfunction plays an essential role in the development of atherosclerosis. We aimed to evaluate the effects of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) on pro-inflammatory tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), angiogenic vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and leukocyte adhesion, intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) and E-selectin in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). In this study, HUVEC cells were treated with 1 and 2 μM of TSH in different treatment times. The gene and protein expression of ICAM-1, VEGF, and E-selectin were performed by real-time polymerase chain reaction and western blotting, respectively. Likewise, TNF-α and IL-6 protein levels were determined by the ELISA method. VEGF, ICAM-1, and E-selectin as endothelial dysfunction markers and also, TNF-α and IL-6 as pro-inflammatory cytokines were detectable in HUVEC. Besides, the results of this study revealed that TSH treatment down-regulates TNF-α and IL-6. Evaluating the gene and protein expression data revealed the upregulation of ICAM-1, E-selectin, and VEGF in TSH treated cases in different periods of exposure. Considering the multiple actions of TSH, it could be concluded that TSH plays a controversial role in atherogenesis by anti-inflammatory effects and on the other side, angiogenesis and leukocyte adhesion induction which is related to vascular cell proliferation.
Keywords: E-selectin; HUVEC; ICAM-1; TNF-α; Thyrotropin; VEGF.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors on cytokine-induced adhesion molecule expression by human umbilical vein endothelial cells.Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Aug;118(7):1761-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb15602.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8842442 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of thyroxine on adhesion molecules and proinflammatory cytokines secretion on human umbilical vein endothelial cells.Res Pharm Sci. 2019 Jun;14(3):237-246. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.258490. Res Pharm Sci. 2019. PMID: 31160901 Free PMC article.
-
[Differential influences of bFGF and VEGF on the expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 on human umbilical vein endothelial cells].Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2000 Feb;23(1):12-21. doi: 10.2177/jsci.23.12. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2000. PMID: 10771568 Japanese.
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor synergistically enhances induction of E-selectin by tumor necrosis factor-alpha.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007 Mar;27(3):494-502. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000255309.38699.6c. Epub 2006 Dec 14. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007. PMID: 17170373
-
Eosinophil transendothelial migration induced by cytokines. I. Role of endothelial and eosinophil adhesion molecules in IL-1 beta-induced transendothelial migration.J Immunol. 1992 Dec 15;149(12):4021-8. J Immunol. 1992. PMID: 1460288
Cited by
-
Atypical pituitary hormone-target tissue axis.Front Med. 2023 Feb;17(1):1-17. doi: 10.1007/s11684-022-0973-7. Epub 2023 Feb 27. Front Med. 2023. PMID: 36849623 Review.
-
Possible effects of Treponema pallidum infection on human vascular endothelial cells.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Apr;36(4):e24318. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24318. Epub 2022 Mar 10. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 35274369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlation analysis of serum thyroid stimulating hormone with acute cerebrovascular disease.Eur J Med Res. 2019 Oct 24;24(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s40001-019-0395-4. Eur J Med Res. 2019. PMID: 31651357 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated Circulating Adipocyte-Fatty Acid Binding Protein Levels Predict Incident Ischemic Cardiovascular Events in a Longitudinal and Prospective AMI Aging Study.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Feb 4;18:1589-1608. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S494049. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 39925937 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation Between Hypothyroidism During Pregnancy and Glucose and Lipid Metabolism in Pregnant Women and Its Influence on Pregnancy Outcome and Fetal Growth and Development.Front Surg. 2022 Mar 28;9:863286. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.863286. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2022. PMID: 35419407 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tian L, Zhang L, Liu J, Guo T, Gao C, Ni J. Effects of TSH on the function of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Clin Mol Endocrinol. 2014;52(2):215–222. - PubMed
-
- Cai Y, Manio MM, Leung GP, Xu A, Tang EH, Vanhoutte PM. Thyroid hormone affects both endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells in rat arteries. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015;747:18–28. - PubMed
-
- Antunes TT, Gagnon A, Bell A, Sorisky A. Thyroid-stimulating hormone stimulates interleukin-6 release from 3T3-L1 adipocytes through a cAMP-protein kinase a pathway. Obes Res. 2005;13(12):2066–2071. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
