Transdermal Evaporation Drug Delivery System: Concept to Commercial Products
- PMID: 30607327
- PMCID: PMC6311647
- DOI: 10.15171/apb.2018.063
Transdermal Evaporation Drug Delivery System: Concept to Commercial Products
Abstract
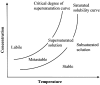
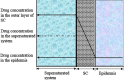
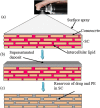
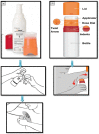
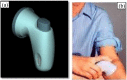
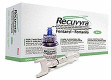
Since two decades or so transdermal route established itself as better alternative to traditional oral route. This is possible due to continuous innovations in transdermal drug delivery (TDD), which not only enables researchers from academia and industry to successfully develop and launch many new pharmaceuticals but also allow to include new classes of drugs that can be developed into transdermal formulations. These successes are achieved due to the use of novel techniques based on either physical or chemical approaches. However, both of these techniques suffer due to their own disadvantages. Comparatively, a simple method of supersaturation to enhance drug permeation across skin has created a new wave of interest. Even though the application supersaturated principle in topical and TDD has been used from 1960s, but proper control of drug release and formation of stable supersaturated states has been the core of intense research in the last decade. Out of various methods used to get supersaturated system, evaporation method is considered as most efficient and practically feasible for TDD. Therefore, in this review concept of supersaturation, selection of solvent system and the mechanism of inhibition of crystallization are discussed. Application of evaporation systems in the development of transdermal formulations such as solutions, semisolids and metered dose therapeutic systems (MDTS) and the commercial evaporative systems are also discussed in this review.
Keywords: Crystallization; Stratum corneum; Supersaturation; Thermodynamic activity; Transdermal.
Figures
References
-
- Parhi R, Suresh P, Pattnaik S. Application of Response Surface Methodology for Design and Optimization of Reservoir-type Transdermal Patch of Simvastatin. Curr Drug Deliv. 2016;13(5):742–53. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources