Overcoming Poor Solubility of Dimenhydrinate: Development, Optimization and Evaluation of Fast Dissolving Oral Film
- PMID: 30607345
- PMCID: PMC6311638
- DOI: 10.15171/apb.2018.081
Overcoming Poor Solubility of Dimenhydrinate: Development, Optimization and Evaluation of Fast Dissolving Oral Film
Abstract
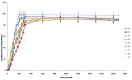
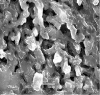
Purpose: To develop fast dissolving oral film to address vomiting and nausea in pediatric population. Methods: Oral films of Dimenhydrinate were prepared by solvent casting method by using hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose E5 (HPMC E5), polyethylene glycol 400 (PEG 400) and croscarmellose sodium. Solubility of dimenhydrinate was enhanced by ethanol as a co-solvent. To make dimenhydrinate palatable sodium saccharin and peppermint oil were used. All films were evaluated for mechanical parameters, surface pH, morphology, disintegration time and percent dissolution. Results: Films were smooth, acceptable and white in colour. For optimized batch, drug content (99.106%), disintegration time (25 sec), dissolution (99.10% in 210 sec), surface pH (6.81) were acceptable. Conclusion: Optimized batch, due to its potential to deliver through fast dissolving film, can be developed for clinical use.
Keywords: Antiemetic; Dimenhydrinate; Fast dissolving film; HPMC E5; Superdisintegrants.
Similar articles
-
Fast-dissolving oral films containing dextromethorphan/phenylephrine for sinusitis treatment: formulation, characterization and optimization.Prog Biomater. 2022 Sep;11(3):243-252. doi: 10.1007/s40204-022-00191-w. Epub 2022 Jul 7. Prog Biomater. 2022. PMID: 35796868 Free PMC article.
-
Formulation and Characterization of Fast-Dissolving Sublingual Film of Iloperidone Using Box-Behnken Design for Enhancement of Oral Bioavailability.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2018 Apr;19(3):1392-1400. doi: 10.1208/s12249-018-0954-y. Epub 2018 Feb 2. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2018. PMID: 29396734
-
Formulation development and evaluation of mouth dissolving film of domperidone.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2012 Mar;4(Suppl 1):S108-9. doi: 10.4103/0975-7406.94159. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2012. PMID: 23066181 Free PMC article.
-
Orally dissolving strips: A new approach to oral drug delivery system.Int J Pharm Investig. 2013 Apr;3(2):67-76. doi: 10.4103/2230-973X.114897. Int J Pharm Investig. 2013. PMID: 24015378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Orodispersible Films: A Systematic Patent Review.Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2018;12(2):110-120. doi: 10.2174/1872211312666180509100216. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2018. PMID: 29745346 Review.
Cited by
-
Preparation, characterization, and in vitro cytogenotoxic evaluation of a novel dimenhydrinate-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex.Biomol Biomed. 2024 Oct 17;24(6):1637-1650. doi: 10.17305/bb.2024.10507. Biomol Biomed. 2024. PMID: 38819319 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Box-Behnken Design in the Preparation, Optimization, and In-Vivo Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Oral Tadalafil-Loaded Niosomal Film.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jan 3;15(1):173. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010173. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36678802 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential of Films as Transmucosal Drug Delivery Systems.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Nov 4;15(11):2583. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15112583. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 38004562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced pharmacokinetic performance of dapoxetine hydrochloride via the formulation of instantly-dissolving buccal films with acidic pH modifier and hydrophilic cyclodextrin: Factorial analysis, in vitro and in vivo assessment.J Adv Res. 2020 May 1;24:281-290. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2020.04.019. eCollection 2020 Jul. J Adv Res. 2020. PMID: 32419956 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Prasanthi NL, Krishna CS, Gupta ME, Manikiran SS, Rao NR. Design and development of sublingual fast dissolving films for an antiasthmatic drug. Der Pharmacia Lett. 2011;3(1):382–95.
-
- Goel H, Rai P, Rana V, Tiwary AK. Orally disintegrating systems: Innovations in formulation and technology. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2008;2(3):258–74. - PubMed
-
- Nehal Siddiqui MD, Garg G, Sharma PK. A Short Review on A novel approach in oral fast dissolving drug delivery system and their patents. Adv Biol Res. 2011;5(6):291–303.
-
- Patel AR, Prajapti DS, Raval JA. Fast dissolving films (FDFs) as a newer venture in fast dosage forms. Int J Drug Dev Res. 2010;2(2):232–46.
-
- Shalini GC, Karwa P, Khanum A, Pandit V. A laconic review on fast dissolving sublingual films as propitious dosage form. Drug delivery lett. 2014;4(1):49–61. doi: 10.2174/22103031113039990010. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources