Is Vitamin D Supplementation Effective in Prevention of Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections in the Pediatrics? A Randomized Triple-Masked Controlled Trial
- PMID: 30607365
- PMCID: PMC6289001
- DOI: 10.4103/abr.abr_149_18
Is Vitamin D Supplementation Effective in Prevention of Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections in the Pediatrics? A Randomized Triple-Masked Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to evaluate the impact of Vitamin D supplementation on prevention of recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs) in the pediatrics.
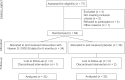
Materials and methods: This randomized, triple-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial was conducted in 2014 among 68 children and adolescents with recurrent UTI. They were randomly assigned to two groups, receiving either Vitamin D (1000 IU/daily) or placebo for 6 months. The serum concentration of Vitamin D before and after the study and the frequency of UTI during the study were recorded.
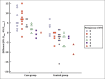
Results: Overall 33 patients in the group of receiving Vitamin D and 32 in the placebo group completed the trial. The mean serum level of Vitamin D had a significant increase in the intervention group (15.80 ± 8.7 vs. 20.56 ± 8.30 ng/mL, P < 0.001) and significant decrease in the placebo group (20.43 ± 13.28 vs. 17.43 ± 9.99 ng/mL, P = 0.041). During the trial, the frequency of UTI was not significantly different between the two groups studied (P = 0.72). Both before and after the trial, the frequency of Vitamin D deficiency, insufficiency, and adequacy was not significantly different within and between groups (P > 0.05).
Conclusion: The findings of this trial revealed that Vitamin D supplementation with the mentioned dose have not significant impact on preventing recurrent UTI. Future studies with higher doses of Vitamin D and longer follow-up are suggested.
Keywords: Children; Vitamin D; prevention; urinary tract infection.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Awais M, Rehman A, Baloch NU, Khan F, Khan N. Evaluation and management of recurrent urinary tract infections in children: State of the art. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2015;13:209–31. - PubMed
-
- Frankul FA, Tawaige ZH, AL-Janabi AA. Urinary tract infections in febrile children. J Fac Med (Baghdad) 2003;45:41–50.
-
- Salo J, Ikäheimo R, Tapiainen T, Uhari M. Childhood urinary tract infections as a cause of chronic kidney disease. Pediatrics. 2011;128:840–7. - PubMed
-
- Williams G, Craig JC. Long-term antibiotics for preventing recurrent urinary tract infection in children? Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Mar;16(3):CD001534. doi: 10.1002/14651858.pub3. - PubMed