Assessment of Right Ventricular Function in Pulmonary Hypertension with Multimodality Imaging
- PMID: 30607386
- PMCID: PMC6310752
- DOI: 10.4250/jcvi.2018.26.e28
Assessment of Right Ventricular Function in Pulmonary Hypertension with Multimodality Imaging
Abstract
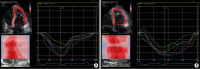
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is defined as resting mean pulmonary artery pressure ≥ 25 mmHg and is caused by multiple etiologies including heart, lung or other systemic diseases. Evaluation of right ventricular (RV) function in PH is very important to plan treatment and determine prognosis. However, quantification of volume and function of the RV remains difficult due to complicated RV geometry. A number of imaging tools has been utilized to diagnose PH and assess RV function. Each imaging technique including conventional echocardiography, three-dimensional echocardiography, strain echocardiography, computed tomography and cardiac magnetic resonance imaging has-advantages and limitations and can provide unique information. In this article, we provide a comprehensive review of the utility, advantages and shortcomings of the multimodality imaging used to evaluate patients with PH.
Keywords: Computed tomography; Echocardiography; Magnetic resonance imaging; Pulmonary hypertension; Right ventricle.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Hoeper MM, Bogaard HJ, Condliffe R, et al. Definitions and diagnosis of pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62:D42–D50. - PubMed
-
- Galiè N, Hoeper MM, Humbert M, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS), endorsed by the International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) Eur Heart J. 2009;30:2493–2537. - PubMed
-
- Moceri P, Baudouy D, Chiche O, et al. Imaging in pulmonary hypertension: Focus on the role of echocardiography. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2014;107:261–271. - PubMed
-
- Alkotob ML, Soltani P, Sheatt MA, et al. Reduced exercise capacity and stress-induced pulmonary hypertension in patients with scleroderma. Chest. 2006;130:176–181. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

