Predictors of nonsentinel lymph node metastasis in patients with breast cancer with metastasis in the sentinel node
- PMID: 30608418
- PMCID: PMC6344180
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013916
Predictors of nonsentinel lymph node metastasis in patients with breast cancer with metastasis in the sentinel node
Abstract
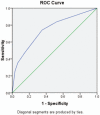
To predict the factors related to axillary nonsentinel lymph node (NSLN) metastasis in patients with positive sentinel lymph node (SLN) of early breast cancer.The retrospective data are collected from the patients with positive SLN who received further completion axillary lymph node dissection (cALND) in Peking Union Medical Hospital between March 2016 and December 2017. Univariate analysis was conducted on data with various clinicopathologic factors at first. Those factors with statistic significance (P < .05) in univariate analysis were then used to implement multivariate analysis and logistic regression.There were total of 734 patients who received SLN biopsy , among whom 153 cases were included in our study. About 39.22% (60/153) of 153 paitents with positive SLN had no NSLN metastasisted to SLN. Univariate analysis showed that 3 variables were significantly correlated with NSLN involvement: tumor size (X = 10.384, P = .001), SLN metastasis ratio (number of positive SLNs/number of SLNs removed × 100%) (X = 10.365, P = .001) and the number of negative sentinel nodes (X = 10.384, P = .006). In multivariate analysis and logistic regression, tumor size (odds ratio [OR] = 3.392, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.409-8.166, P = .006) and SLN metastasis ratio (OR = 3.514, 95% CI: 1.416-8.72, P = .007) were the independent risk factors. While the number of negative sentinel nodes (OR = 0.211, 95% CI: 0.063-0.709, P = .014) was the independent protective factor. The calculated risk resulted in an area under the curve of 0.746 (95% CI: 0.644-0.848), suggesting stable discriminative capability in Chinese population.For those patients with positive SLN, larger tumor burden and SLN metastasis ratio are independent risk factors for NSLN metastasis. However, the more of the detected negative SLN, the less possibility with NSLN involvement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Positive non-sentinel axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer with 1-2 sentinel lymph node metastases.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Nov;97(44):e13015. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013015. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30383658 Free PMC article.
-
[A nomogram to predict non-sentinel lymph node metastasis for breast cancer patients with positive axillary sentinel lymph node].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2020 Aug 23;42(8):653-659. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20190824-00545. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32867457 Chinese.
-
Prediction of non-sentinel lymph node involvement in breast cancer patients with a positive sentinel lymph node.Breast. 2014 Aug;23(4):453-9. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2014.03.009. Epub 2014 Apr 24. Breast. 2014. PMID: 24768478
-
A quantitative analysis of tumour characteristics in breast cancer patients with extranodal extension in non-sentinel nodes.Breast. 2018 Apr;38:171-174. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2018.01.003. Epub 2018 Feb 3. Breast. 2018. PMID: 29413405 Review.
-
The diagnostic accuracy of intraoperative frozen section biopsy for diagnosis of sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients: a meta-analysis.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 Jul;29(32):47931-47941. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-20569-4. Epub 2022 May 11. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35543788 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Establishing a prediction model of axillary nodal burden based on the combination of CT and ultrasound findings and the clinicopathological features in patients with early-stage breast cancer.Gland Surg. 2021 Feb;10(2):751-760. doi: 10.21037/gs-20-899. Gland Surg. 2021. PMID: 33708557 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of negative axillary node clearance by sentinel node-positive to total node ratio: a retrospective cohort study.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023 Aug 7;85(10):4689-4693. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000000932. eCollection 2023 Oct. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023. PMID: 37811068 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of an ultrasonography and clinicopathological features-based nomogram for non-sentinel lymph node metastasis.Gland Surg. 2023 Mar 31;12(3):402-414. doi: 10.21037/gs-23-58. Epub 2023 Mar 24. Gland Surg. 2023. PMID: 37057045 Free PMC article.
-
Association between postoperative pathological results and non-sentinel nodal metastasis in breast cancer patients with sentinel lymph node-positive breast cancer.World J Surg Oncol. 2024 Jan 24;22(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s12957-024-03306-8. World J Surg Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38268018 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors of non-sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer with 1-2 sentinel lymph node macrometastases underwent total mastectomy: a case-control study.World J Surg Oncol. 2023 Apr 6;21(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s12957-023-02888-z. World J Surg Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37024930 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chalasani P, Downey L, Stopeck AT. Caring for the breast cancer survivor: a guide for primary care physicians. Am J Med 2010;123:489–95. - PubMed
-
- Ding B, Qian L, Zhao Y, et al. Meta-analysis of endoscopic axillary lymph node dissection versus conventional open excision for breast cancer [in Chinese]. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2015;40:782–9. - PubMed
-
- Krag DN, Anderson SJ, Julian TB, et al. Sentinel-lymph-node resection compared with conventional axillary-lymph-node dissection in clinically node-negative patients with breast cancer: overall survival findings from the NSABP B-32 randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2010;11:927–33. - PMC - PubMed
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN). Clinical practices guidelines in oncology: breast cancer, version 2.2012. Available at: http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/breast.pdf Accessed August 20, 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

