Neurotrophins and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in the ovary: physiological and pathophysiological implications
- PMID: 30608586
- PMCID: PMC6390169
- DOI: 10.1093/humupd/dmy047
Neurotrophins and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in the ovary: physiological and pathophysiological implications
Abstract
Background: Neurotrophins [nerve growth factor (NGF), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), neurotrophin-3 (NT-3), and neurotrophin-4 (NT-4)] and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) are soluble polypeptide growth factors that are widely recognized for their roles in promoting cell growth, survival and differentiation in several classes of neurons. Outside the nervous system, neurotrophin (NT) and GDNF signaling events have substantial roles in various non-neural tissues, including the ovary.
Objective and rationale: The molecular mechanisms that promote and regulate follicular development and oocyte maturation have been extensively investigated. However, most information has been obtained from animal models. Even though the fundamental process is highly similar across species, the paracrine regulation of ovarian function in humans remains poorly characterized. Therefore, this review aims to summarize the expression and functional roles of NTs and GDNF in human ovarian biology and disorders, and to describe and propose the development of novel strategies for diagnosing, treating and preventing related abnormalities.
Search methods: Relevant literature in the English language from 1990 to 2018 describing the role of NTs and GDNF in mammalian ovarian biology and phenotypes was comprehensively selected using PubMed, MEDLINE and Google Scholar.
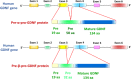
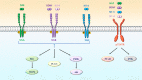
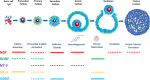
Outcomes: Studies have shown that the neurotrophins NGF, BDNF, NT-3 and NT-4 as well as GDNF and their functional receptors are expressed in the human ovary. Recently, gathered experimental data suggest putative roles for NT and GDNF signaling in the direct control of ovarian function, including follicle assembly, activation of the primordial follicles, follicular growth and development, oocyte maturation, steroidogenesis, ovulation and corpus luteum formation. Additionally, crosstalk occurs between these ovarian regulators and the endocrine signaling system. Dysregulation of the NT system may negatively affect ovarian function, leading to reproductive pathology (decreased ovarian reserve, polycystic ovary syndrome and endometriosis), female infertility and even epithelial ovarian cancers.
Wider implications: A comprehensive understanding of the expression, actions and underlying molecular mechanisms of the NT/GDNF system in the human ovary is essential for novel approaches to therapeutic and diagnostic interventions in ovarian diseases and to develop more safe, effective methods of inducing ovulation in ART in the treatment of female infertility.
Keywords: brain-derived neurotrophic factor; diminished ovarian reserve; endometriosis; female infertility; follicular development; glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor; nerve growth factor; neurotrophins; polycystic ovary syndrome.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The importance of neuronal growth factors in the ovary.Mol Hum Reprod. 2016 Jan;22(1):3-17. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gav057. Epub 2015 Oct 20. Mol Hum Reprod. 2016. PMID: 26487421 Review.
-
Oocyte-somatic cell interactions in the human ovary-novel role of bone morphogenetic proteins and growth differentiation factors.Hum Reprod Update. 2016 Dec;23(1):1-18. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmw039. Epub 2016 Oct 26. Hum Reprod Update. 2016. PMID: 27797914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The roles of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor during the final stage of folliculogenesis: a focus on oocyte maturation.Reproduction. 2013 Jan 24;145(2):R43-54. doi: 10.1530/REP-12-0219. Print 2013 Feb. Reproduction. 2013. PMID: 23166367 Review.
-
Neurotrophic and cell-cell dependent control of early follicular development.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2000 May 25;163(1-2):67-71. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(99)00242-7. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2000. PMID: 10963876 Review.
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression and function in the mammalian reproductive Tract.Hum Reprod Update. 2020 Jun 18;26(4):545-564. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmaa008. Hum Reprod Update. 2020. PMID: 32378708
Cited by
-
Single‑cell RNA sequencing analysis of human embryos from the late Carnegie to fetal development.Cell Biosci. 2024 Sep 12;14(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s13578-024-01302-9. Cell Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39267141 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Effects of Nanowired Delivery of Cerebrolysin with Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Monoclonal Antibodies to Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase in Brain Pathology Following Alzheimer's Disease Exacerbated by Concussive Head Injury.Adv Neurobiol. 2023;32:139-192. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-32997-5_4. Adv Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37480461 Review.
-
NTRK2 Promotes Sheep Granulosa Cells Proliferation and Reproductive Hormone Secretion and Activates the PI3K/AKT Pathway.Animals (Basel). 2024 May 14;14(10):1465. doi: 10.3390/ani14101465. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38791682 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of miR-10a-5p and miR-103a-3p, Regulators of BDNF Expression in Follicular Fluid, in the Outcomes of IVF-ET.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 May 12;12:637384. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.637384. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34054723 Free PMC article.
-
Moderate Aerobic Exercise Regulates Follicular Dysfunction by Initiating Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF)-Mediated Anti-Apoptotic Signaling Pathways in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.J Clin Med. 2022 Sep 23;11(19):5584. doi: 10.3390/jcm11195584. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36233452 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abir R, Fisch B, Jin S, Barnnet M, Ben-Haroush A, Felz C, Kessler-Icekson G, Feldberg D, Nitke S, Ao A. Presence of NGF and its receptors in ovaries from human fetuses and adults. Mol Hum Reprod 2005;11:229–236. - PubMed
-
- Adams GP, Ratto MH, Huanca W, Singh J. Ovulation-inducing factor in the seminal plasma of alpacas and llamas. Biol Reprod 2005;73:452–457. - PubMed
-
- Adhikari D, Liu K. Molecular mechanisms underlying the activation of mammalian primordial follicles. Endocr Rev 2009;30:438–464. - PubMed
-
- Airaksinen MS, Saarma M. The GDNF family: signalling, biological functions and therapeutic value. Nat Rev Neurosci 2002;3:383–394. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

