Development of the covalent antibody-DNA conjugates technology for detection of IgE and IgM antibodies by immuno-PCR
- PMID: 30608947
- PMCID: PMC6319726
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0209860
Development of the covalent antibody-DNA conjugates technology for detection of IgE and IgM antibodies by immuno-PCR
Abstract
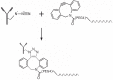
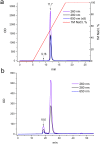
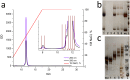
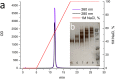
Immuno-PCR (iPCR) is one of the methods used for the detection of a wide range of analytes and features the high sensitivity of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method. iPCR uses antibodies coupled to DNA, followed by the amplification of the attached DNA using RT-PCR. Two major types of antibody-DNA conjugates are currently used, which are obtained as a result of non-covalent (biotin-streptavidin) or covalent interactions. Using a strain-promoted azide-alkyne cycloaddition (SPAAC), we synthesized covalent DNA-antibody conjugates, optimized the reaction conditions, and developed an efficient protocol for the purification of conjugates, with which all unreacted antibodies and oligonucleotides are separated. Covalent DNA-antibody conjugates were tested with iPCR assays that were previously developed for the detection of IgE and IgM antibodies with the use of the supramolecular complex of 5'- and 3'-biotinylated DNA and streptavidin. The results show that the modification of antibodies with amino groups did not allow us to obtain monolabeled antibodies or antibodies with a strictly defined number of DNA-labels. The degree of labeling determined by the dyes introduced through the azido group reflects the actual labeling degree statistically. If the average labeling degree for azido groups is 1.1, the conjugates contain 25% mono-labeled antibodies, 50% double-labeled antibodies, and 25% unlabeled ones. The specificity of the monoclonal antibody to human IgE (BE5) changed after conjugation with the oligonucleotide. The sensitivity of iPCR in the detection of IgM antibodies produced against the LeC disaccharide using a covalent conjugate was similar to that of a supramolecular complex of 5'- and 3'-biotinylated DNA and streptavidin, but the new procedure is two steps shorter.
Conflict of interest statement
AVM is employed by a commercial company: OOO DNA-Technology TS, Moscow. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures

References
-
- Sano T, Smith CL, Cantor CR. Immuno-PCR: very sensitive antigen detection by means of specific antibody-DNA conjugates. Science. 1992;258, 120–122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

