A Review on Quantitative Multiplexed Proteomics
- PMID: 30609196
- PMCID: PMC6520187
- DOI: 10.1002/cbic.201800650
A Review on Quantitative Multiplexed Proteomics
Abstract
Over the last few decades, mass spectrometry-based proteomics has become an increasingly powerful tool that is now able to routinely detect and quantify thousands of proteins. A major advance for global protein quantification was the introduction of isobaric tags, which, in a single experiment, enabled the global quantification of proteins across multiple samples. Herein, these methods are referred to as multiplexed proteomics. The principles, advantages, and drawbacks of various multiplexed proteomics techniques are discussed and compared with alternative approaches. We also discuss how the emerging combination of multiplexing with targeted proteomics might enable the reliable and high-quality quantification of very low abundance proteins across multiple conditions. Lastly, we suggest that fusing multiplexed proteomics with data-independent acquisition approaches might enable the comparison of hundreds of different samples without missing values, while maintaining the superb measurement precision and accuracy obtainable with isobaric tag quantification.
Keywords: analytical methods; isotopic labeling; mass spectrometry; proteins; proteomics.
© 2019 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures


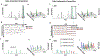


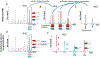
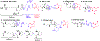
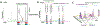
References
-
- Ardrey RE, Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry: an introduction, J. Wiley, New York, 2003.
-
- Olsen JV, Ong SE, Mann M, Mol Cell Proteomics 2004, 3, 608–614. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

