Roco Proteins: GTPases with a Baroque Structure and Mechanism
- PMID: 30609797
- PMCID: PMC6337361
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20010147
Roco Proteins: GTPases with a Baroque Structure and Mechanism
Abstract
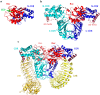
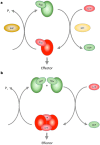
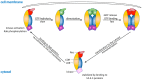
Mutations in leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) are a common cause of genetically inherited Parkinson's Disease (PD). LRRK2 is a large, multi-domain protein belonging to the Roco protein family, a family of GTPases characterized by a central RocCOR (Ras of complex proteins/C-terminal of Roc) domain tandem. Despite the progress in characterizing the GTPase function of Roco proteins, there is still an ongoing debate concerning the working mechanism of Roco proteins in general, and LRRK2 in particular. This review consists of two parts. First, an overview is given of the wide evolutionary range of Roco proteins, leading to a variety of physiological functions. The second part focusses on the GTPase function of the RocCOR domain tandem central to the action of all Roco proteins, and progress in the understanding of its structure and biochemistry is discussed and reviewed. Finally, based on the recent work of our and other labs, a new working hypothesis for the mechanism of Roco proteins is proposed.
Keywords: GTPase mechanism; Parkinson’s disease; Roco proteins; leucine-rich repeat kinase 2; unconventional G-protein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

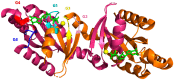
Similar articles
-
Revisiting the Roco G-protein cycle.Biochem J. 2015 Jan 1;465(1):139-47. doi: 10.1042/BJ20141095. Biochem J. 2015. PMID: 25317655
-
Understanding the GTPase Activity of LRRK2: Regulation, Function, and Neurotoxicity.Adv Neurobiol. 2017;14:71-88. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-49969-7_4. Adv Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 28353279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Roc-COR tandem domain of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 forms dimers and exhibits conventional Ras-like GTPase properties.J Neurochem. 2018 Nov;147(3):409-428. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14566. J Neurochem. 2018. PMID: 30091236
-
Conformational heterogeneity of the Roc domains in C. tepidum Roc-COR and implications for human LRRK2 Parkinson mutations.Biosci Rep. 2015 Aug 26;35(5):e00254. doi: 10.1042/BSR20150128. Biosci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26310572 Free PMC article.
-
The unconventional G-protein cycle of LRRK2 and Roco proteins.Biochem Soc Trans. 2016 Dec 15;44(6):1611-1616. doi: 10.1042/BST20160224. Biochem Soc Trans. 2016. PMID: 27913669 Review.
Cited by
-
LRRK2 Biology from structure to dysfunction: research progresses, but the themes remain the same.Mol Neurodegener. 2019 Dec 21;14(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s13024-019-0344-2. Mol Neurodegener. 2019. PMID: 31864390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanobodies as allosteric modulators of Parkinson's disease-associated LRRK2.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Mar 1;119(9):e2112712119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2112712119. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35217606 Free PMC article.
-
LRRK2 Knockout Confers Resistance in HEK-293 Cells to Rotenone-Induced Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Damage, and Apoptosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 22;24(13):10474. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310474. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445652 Free PMC article.
-
Oligomerization of Lrrk controls actin severing and α-synuclein neurotoxicity in vivo.Mol Neurodegener. 2021 May 24;16(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s13024-021-00454-3. Mol Neurodegener. 2021. PMID: 34030727 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse Physiological Functions and Regulatory Mechanisms for Signal-Transducing Small GTPases.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 2;21(19):7291. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197291. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33023216 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parkinson J. An Essay on the Shaking Palsy. Whittingham and Rowland for Sherwood, Neely and Jones; London, UK: 1817.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

