An Update on the Effects of Glyceollins on Human Health: Possible Anticancer Effects and Underlying Mechanisms
- PMID: 30609801
- PMCID: PMC6357109
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11010079
An Update on the Effects of Glyceollins on Human Health: Possible Anticancer Effects and Underlying Mechanisms
Abstract
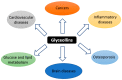
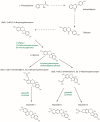
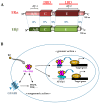
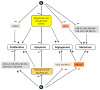
Biologically active plant-based compounds, commonly referred to as phytochemicals, can influence the expression and function of various receptors and transcription factors or signaling pathways that play vital roles in cellular functions and are then involved in human health and diseases. Thus, phytochemicals may have a great potential to prevent and treat chronic diseases. Glyceollins, a group of phytoalexins that are isolated from soybeans, have attracted attention because they exert numerous effects on human functions and diseases, notably anticancer effects. In this review, we have presented an update on the effects of glyceollins in relation to their potential beneficial roles in human health. Despite a growing number of studies suggesting that this new family of phytochemicals can be involved in critical cellular pathways, such as estrogen receptor, protein kinase, and lipid kinase signaling pathways, future investigations will be needed to better understand their molecular mechanisms and their specific significance in biomedical applications.
Keywords: breast cancer; dietary compounds; estrogen receptor; glyceollins; human health; phytochemicals; signaling pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Knaze V., Rothwell J.A., Zamora-Ros R., Moskal A., Kyrø C., Jakszyn P., Skeie G., Weiderpass E., Santucci de Magistris M., Agnoli C., et al. A new food-composition database for 437 polyphenols in 19,899 raw and prepared foods used to estimate polyphenol intakes in adults from 10 European countries. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018;108:517–524. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqy098. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

