Contributions and Challenges of High Throughput qPCR for Determining Antimicrobial Resistance in the Environment: A Critical Review
- PMID: 30609875
- PMCID: PMC6337382
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24010163
Contributions and Challenges of High Throughput qPCR for Determining Antimicrobial Resistance in the Environment: A Critical Review
Abstract
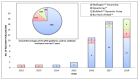
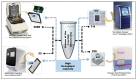
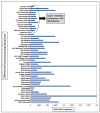
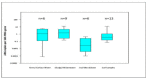
Expansion in whole genome sequencing and subsequent increase in antibiotic resistance targets have paved the way of high throughput qPCR (HT-qPCR) for analyzing hundreds of antimicrobial resistance genes (ARGs) in a single run. A meta-analysis of 51 selected studies is performed to evaluate ARGs abundance trends over the last 7 years. WaferGenTM SmartChip is found to be the most widely used HT-qPCR platform among others for evaluating ARGs. Up till now around 1000 environmental samples (excluding biological replicates) from different parts of the world have been analyzed on HT-qPCR. Calculated detection frequency and normalized ARGs abundance (ARGs/16S rRNA gene) reported in gut microbiome studies have shown a trend of low ARGs as compared to other environmental matrices. Disparities in the HT-qPCR data analysis which are causing difficulties to researchers in precise interpretation of results have been highlighted and a possible way forward for resolving them is also suggested. The potential of other amplification technologies and point of care or field deployable devices for analyzing ARGs have also been discussed in the review. Our review has focused on updated information regarding the role, current status and future perspectives of HT-qPCR in the field of antimicrobial resistance.
Keywords: AMR; ARGs; MGEs; gut microbiome; high throughput qPCR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Metagenomic next generation sequencing for studying antibiotic resistance genes in the environment.Adv Appl Microbiol. 2023;123:41-89. doi: 10.1016/bs.aambs.2023.05.001. Epub 2023 May 30. Adv Appl Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37400174
-
Feed additives shift gut microbiota and enrich antibiotic resistance in swine gut.Sci Total Environ. 2018 Apr 15;621:1224-1232. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.106. Epub 2017 Oct 18. Sci Total Environ. 2018. PMID: 29054657
-
The impacts of different high-throughput profiling approaches on the understanding of bacterial antibiotic resistance genes in a freshwater reservoir.Sci Total Environ. 2019 Nov 25;693:133585. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133585. Epub 2019 Jul 24. Sci Total Environ. 2019. PMID: 31377359
-
Recent advances in environmental antibiotic resistance genes detection and research focus: From genes to ecosystems.Environ Int. 2024 Sep;191:108989. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2024.108989. Epub 2024 Aug 29. Environ Int. 2024. PMID: 39241334 Review.
-
Functional Metagenomics as a Tool for Identification of New Antibiotic Resistance Genes from Natural Environments.Microb Ecol. 2017 Feb;73(2):479-491. doi: 10.1007/s00248-016-0866-x. Epub 2016 Oct 5. Microb Ecol. 2017. PMID: 27709246 Review.
Cited by
-
Enlarging the Toolbox Against Antimicrobial Resistance: Aptamers and CRISPR-Cas.Front Microbiol. 2021 Feb 19;12:606360. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.606360. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33679633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Updates on developing and applying biosensors for the detection of microorganisms, antimicrobial resistance genes and antibiotics: a scoping review.Front Public Health. 2023 Sep 7;11:1240584. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1240584. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37744478 Free PMC article.
-
Water, Water Everywhere, but Every Drop Unique: Challenges in the Science to Understand the Role of Contaminants of Emerging Concern in the Management of Drinking Water Supplies.Geohealth. 2023 Dec 28;7(12):e2022GH000716. doi: 10.1029/2022GH000716. eCollection 2023 Dec. Geohealth. 2023. PMID: 38155731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of the emergence of antibiotic resistance in bioaerosols and its monitoring methods.Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol. 2022;21(3):799-827. doi: 10.1007/s11157-022-09622-3. Epub 2022 Jun 6. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35694630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into kinetic and regression models developed to estimate the abundance of antibiotic-resistant genes during biological digestion of wastewater sludge.J Water Health. 2025 Feb;23(2):238-259. doi: 10.2166/wh.2025.372. Epub 2025 Jan 22. J Water Health. 2025. PMID: 40018965 Review.
References
-
- Ciorba V., Odone A., Veronesi L., Pasquarella C., Signorelli C. Antibiotic resistance as a major public health concern: Epidemiology and economic impact. Ann. Ig. 2015;27:562–579. - PubMed
-
- Aubertheau E., Stalder T., Mondamert L., Ploy M.-C., Dagot C., Labanowski J. Impact of wastewater treatment plant discharge on the contamination of river biofilms by pharmaceuticals and antibiotic resistance. Sci. Total Environ. 2017;579:1387–1398. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.11.136. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

