Epigenetically upregulated oncoprotein PLCE1 drives esophageal carcinoma angiogenesis and proliferation via activating the PI-PLCε-NF-κB signaling pathway and VEGF-C/ Bcl-2 expression
- PMID: 30609930
- PMCID: PMC6320601
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-018-0930-x
Epigenetically upregulated oncoprotein PLCE1 drives esophageal carcinoma angiogenesis and proliferation via activating the PI-PLCε-NF-κB signaling pathway and VEGF-C/ Bcl-2 expression
Abstract
Background: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is one of the most lethal malignancies. Neovascularization during tumorigenesis supplies oxygen and nutrients to proliferative tumor cells, and serves as a conduit for migration. Targeting oncogenes involved in angiogenesis is needed to treat organ-confined and locally advanced ESCC. Although the phospholipase C epsilon-1 (PLCE1) gene was originally identified as a susceptibility gene for ESCC, how PLCE1 is involved in ESCC is unclear.
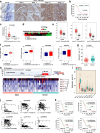
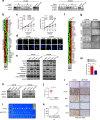
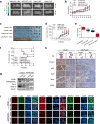
Methods: Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry were used to measure the methylation status of the PLCE1 promoter region. To validate the underlying mechanism for PLCE1 in constitutive activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway, we performed studies using in vitro and in vivo assays and samples from 368 formalin-fixed esophageal cancer tissues and 215 normal tissues with IHC using tissue microarrays and the Cancer Genome Atlas dataset.
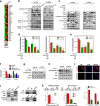
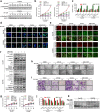
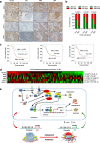
Results: We report that hypomethylation-associated up-regulation of PLCE1 expression was correlated with tumor angiogenesis and poor prognosis in ESCC cohorts. PLCE1 can activate NF-κB through phosphoinositide-phospholipase C-ε (PI-PLCε) signaling pathway. Furthermore, PLCE1 can bind p65 and IκBα proteins, promoting IκBα-S32 and p65-S536 phosphorylation. Consequently, phosphorylated IκBα promotes nuclear translocation of p50/p65 and p65, as a transcription factor, can bind vascular endothelial growth factor-C and bcl-2 promoters, enhancing angiogenesis and inhibiting apoptosis in vitro. Moreover, xenograft tumors in nude mice proved that PLCE1 can induce angiogenesis, inhibit apoptosis, and increase tumor aggressiveness via the NF-κB signaling pathway in vivo.
Conclusions: Our findings not only provide evidence that hypomethylation-induced PLCE1 confers angiogenesis and proliferation in ESCC by activating PI-PLCε-NF-κB signaling pathway and VEGF-C/Bcl-2 expression, but also suggest that modulation of PLCE1 by epigenetic modification or a selective inhibitor may be a promising therapeutic approach for the treatment of ESCC.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Esophageal carcinoma; NF-κB; PLCE1; Proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All experiments were approved by the Ethics Committee of The First Affiliated Hospital, Shihezi University School of Medicine.
Consent for publication
All authors give consent for the publication of the manuscript in
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hypomethylation-Linked Activation of PLCE1 Impedes Autophagy and Promotes Tumorigenesis through MDM2-Mediated Ubiquitination and Destabilization of p53.Cancer Res. 2020 Jun 1;80(11):2175-2189. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-1912. Epub 2020 Feb 17. Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32066565
-
Protocadherin 8 (PCDH8) Inhibits Proliferation, Migration, Invasion, and Angiogenesis in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Apr 24;26:e920665. doi: 10.12659/MSM.920665. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32330123 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated expression patterns and tight correlation of the PLCE1 and NF-κB signaling in Kazakh patients with esophageal carcinoma.Med Oncol. 2014 Jan;31(1):791. doi: 10.1007/s12032-013-0791-5. Epub 2013 Dec 5. Med Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24307345
-
Roles of oncogenes in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and their therapeutic potentials.Clin Transl Oncol. 2023 Mar;25(3):578-591. doi: 10.1007/s12094-022-02981-x. Epub 2022 Oct 31. Clin Transl Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36315334 Review.
-
Prognostic value of microvessel density in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma-a systematic review and meta-analysis.Pathol Res Pract. 2021 Nov;227:153644. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2021.153644. Epub 2021 Oct 5. Pathol Res Pract. 2021. PMID: 34634564
Cited by
-
Silencing lncRNA AFAP1-AS1 Inhibits the Progression of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells via Regulating the miR-498/VEGFA Axis.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Jul 29;12:6397-6409. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S254302. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 32801880 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNAs in renal cell carcinoma: from mechanistic to clinical perspective.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Nov 22;23(1):288. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-03128-w. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 37993909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prospect of exosomal circular RNAs in breast Cancer: presents and future.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jul;49(7):6997-7011. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07472-4. Epub 2022 May 9. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35534582 Review.
-
A micropeptide XBP1SBM encoded by lncRNA promotes angiogenesis and metastasis of TNBC via XBP1s pathway.Oncogene. 2022 Apr;41(15):2163-2172. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02229-6. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Oncogene. 2022. PMID: 35197570
-
lncRNA-PLACT1 sustains activation of NF-κB pathway through a positive feedback loop with IκBα/E2F1 axis in pancreatic cancer.Mol Cancer. 2020 Feb 21;19(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01153-1. Mol Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32085715 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

