Mobile Phone-Based Telemedicine Practice in Older Chinese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 30609983
- PMCID: PMC6682265
- DOI: 10.2196/10664
Mobile Phone-Based Telemedicine Practice in Older Chinese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: Previous studies on telemedicine interventions have shown that older diabetic patients experience difficulty in using computers, which is a barrier to remote communication between medical teams and older diabetic patients. However, older people in China tend to find it easy to use mobile phones and personal messaging apps that have a user-friendly interface. Therefore, we designed a mobile health (mHealth) system for older people with diabetes that is based on mobile phones, has a streamlined operation interface, and incorporates maximum automation.
Objective: The goal of the research was to investigate the use of mobile phone-based telemedicine apps for management of older Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Variables of interest included efficacy and safety.
Methods: A total of 91 older (aged over 65 years) patients with T2DM who presented to our department were randomly assigned to one of two groups. Patients in the intervention group (n=44) were provided glucometers capable of data transmission and received advice pertaining to medication, diet, and exercise via the mHealth telemedicine system. Patients assigned to the control group (n=47) received routine outpatient care with no additional intervention. Patients in both groups were followed up at regular 3-month intervals.
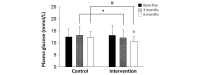
Results: After 3 months, patients in the intervention group showed significant (P<.05) improvement in postprandial plasma glucose level. After 6 months, patients in the intervention group exhibited a decreasing trend in postprandial plasma glucose and glycated hemoglobin levels compared with the baseline and those in the control group (P<.05).
Conclusions: Mobile phone-based telemedicine apps help improve glycemic control in older Chinese patients with T2DM.
Trial registration: China Clinical Trial Registration Center ChiCTR 1800015214; http://www.chictr.org.cn/showprojen.aspx?proj=25949 (Archived by WebCite at http://www.webcitation.org/73wKj1GMq).
Keywords: health management; telemedicine; type 2 diabetes.
©Chenglin Sun, Lin Sun, Shugang Xi, Hong Zhang, Huan Wang, Yakun Feng, Yufeng Deng, Haimin Wang, Xianchao Xiao, Gang Wang, Yuan Gao, Guixia Wang. Originally published in JMIR Mhealth and Uhealth (http://mhealth.jmir.org), 04.01.2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures


References
-
- Xu Y, Wang L, He J, Bi Y, Li M, Wang T, Wang L, Jiang Y, Dai M, Lu J, Xu M, Li Y, Hu N, Li J, Mi S, Chen C, Li G, Mu Y, Zhao J, Kong L, Chen J, Lai S, Wang W, Zhao W, Ning G, 2010 China Noncommunicable Disease Surveillance Group Prevalence and control of diabetes in Chinese adults. JAMA. 2013 Sep 04;310(9):948–959. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.168118. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Remler DK, Teresi JA, Weinstock RS, Ramirez M, Eimicke JP, Silver S, Shea S. Health care utilization and self-care behaviors of Medicare beneficiaries with diabetes: comparison of national and ethnically diverse underserved populations. Popul Health Manag. 2011 Feb;14(1):11–20. doi: 10.1089/pop.2010.0003. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/21241171 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kirkman MS, Briscoe VJ, Clark N, Florez H, Haas LB, Halter JB, Huang ES, Korytkowski MT, Munshi MN, Odegard PS, Pratley RE, Swift CS, Consensus Development Conference on Diabetes and Older Adults Diabetes in older adults: a consensus report. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2012 Dec;60(12):2342–2356. doi: 10.1111/jgs.12035. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/23106132 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, Diamant M, Ferrannini E, Nauck M, Peters AL, Tsapas A, Wender R, Matthews DR, American Diabetes Association (ADA) European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a patient-centered approach: position statement of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) Diabetes Care. 2012 Jun;35(6):1364–1379. doi: 10.2337/dc12-0413. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/22517736 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

