Attitudes and behaviour towards psychotropic drug prescribing in Swedish primary care: a questionnaire study
- PMID: 30611211
- PMCID: PMC6321667
- DOI: 10.1186/s12875-018-0885-4
Attitudes and behaviour towards psychotropic drug prescribing in Swedish primary care: a questionnaire study
Abstract
Background: The prescribing of psychotropic drugs, i.e. antidepressants, sedatives (anxiolytics, hypnotics), and antipsychotics is considerable and a large proportion is prescribed by general practitioners (GPs). There are concerns about dependency and medicalisation, and treatment decisions in psychiatry may appear arbitrary. Increased knowledge of GPs' opinions on the prescribing of psychotropics may lead to more rational use of these drugs. We aimed to quantify GPs' attitudes, beliefs and behaviour towards various aspects of psychotropic drug prescribing.
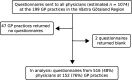
Methods: A questionnaire was distributed to physicians in all 199 GP practices in Region Västra Götaland, Sweden. The questions concerned determinants of psychotropic drug prescribing that had been identified in a previous, qualitative study.
Results: Questionnaires from 516 physicians (64% of whom were specialists in family medicine, 21% interns in family medicine, 15% others) at 152 GP practices (59% of which were state owned, 72% in an urban area, with a median of 7808 registered patients) were returned (estimated response rate: 48%). A majority - 62% - of GPs found it easier to start prescribing psychotropic drugs than to stop (95% confidence interval, 57%, 66%) vs. 8% (6%, 10%). Most GPs considered psychotherapy more suitable than psychotropic drugs in cases of mild psychiatric disease: 81% (77%, 84%) vs. 4% (3%, 6%). The problems treated with psychotropic drugs were considered to be mostly socioeconomic, or mostly medical, by similar proportions of physicians: 38% (34%, 42%) vs. 40% (36%, 45%). GPs were on average satisfied with their levels of antidepressant and sedative prescribing in relation to medical needs. More GPs regarded their prescribing of antipsychotics as being too low rather than too high: 33% (28%, 39%) vs. 7% (4%, 10%).
Conclusions: This study illustrates the complexities of psychiatric drug treatment in primary care and identifies potential drivers of increased prescribing of psychotropics. The manifold factors, medical and non-medical, that affect prescribing decisions may explain a sense of arbitrariness surrounding psychotropic drug treatment. This notwithstanding, GPs seem mostly content with their prescribing.
Keywords: Prescribing; Primary health care; Psychotropic drugs; Questionnaire.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study protocol was approved by the Regional Ethical Review Board in Gothenburg, Sweden (reference number: 777–10). Consent to participate was implicit in the returning of a questionnaire.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Similar articles
-
"Psychiatry is not a science like others" - a focus group study on psychotropic prescribing in primary care.BMC Fam Pract. 2013 Aug 12;14:115. doi: 10.1186/1471-2296-14-115. BMC Fam Pract. 2013. PMID: 23937398 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in prescription of psychotropic medications to children and adolescents in Australian primary care from 2011 to 2018.Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2022 Nov;56(11):1477-1490. doi: 10.1177/00048674211067720. Epub 2021 Dec 28. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 34963342
-
Trends in GP prescribing of psychotropic medications among young patients aged 16-24 years: a case study analysis.BMC Psychiatry. 2017 Jun 6;17(1):214. doi: 10.1186/s12888-017-1375-2. BMC Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28587610 Free PMC article.
-
A qualitative literature review exploring the drivers influencing antibiotic over-prescribing by GPs in primary care and recommendations to reduce unnecessary prescribing.Perspect Public Health. 2021 Jan;141(1):19-27. doi: 10.1177/1757913919879183. Epub 2019 Oct 21. Perspect Public Health. 2021. PMID: 31633458 Review.
-
A cross-sectional prevalence survey of psychotropic medication prescribing patterns in prisons in England.Southampton (UK): NIHR Journals Library; 2014 Sep. Southampton (UK): NIHR Journals Library; 2014 Sep. PMID: 25642536 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Yonder: District nursing, deprescribing, psychotropic drugs, and reasonableness.Br J Gen Pract. 2019 Feb;69(679):78. doi: 10.3399/bjgp19X701033. Br J Gen Pract. 2019. PMID: 30705005 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Prepandemic psychotropic drug status in Portugal: a nationwide pharmacoepidemiological profile.Sci Rep. 2023 Apr 27;13(1):6912. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-33765-0. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37106018 Free PMC article.
-
Mental-Illness-Related Stigma in Health Care in South India: Mixed-Methods Study.Indian J Psychol Med. 2021 Jan;43(1):58-64. doi: 10.1177/0253717620932244. Epub 2020 Jul 20. Indian J Psychol Med. 2021. PMID: 34349308 Free PMC article.
-
Descriptive Study of Patients Treated in a Psychosomatic Internal Medicine Declared by Japanese Family Medicine Clinic.J Clin Med Res. 2023 Jul;15(7):360-367. doi: 10.14740/jocmr4939. Epub 2023 Jul 31. J Clin Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37575353 Free PMC article.
-
Different Attitudes of Patients and Psychiatrists Toward Benzodiazepine Treatment.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2021 Jun 15;17:1927-1936. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S314440. eCollection 2021. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2021. PMID: 34163166 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vos T, Abajobir AA, Abate KH, Abbafati C, Abbas KM, Abd-Allah F, et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2016. Lancet. 2017;390(10100):1211–1259. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32154-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Försäkringskassan . Socialförsäkringsrapport [Social Insurance Report] 2017. p. 2017.
-
- Abbing-Karahagopian V, Huerta C, Souverein PC, de Abajo F, Leufkens HGM, Slattery J, et al. Antidepressant prescribing in five European countries: application of common definitions to assess the prevalence, clinical observations, and methodological implications. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2014;70(7):849–857. doi: 10.1007/s00228-014-1676-z. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Huerta C, Abbing-Karahagopian V, Requena G, Oliva B, Alvarez Y, Gardarsdottir H, et al. Exposure to benzodiazepines (anxiolytics, hypnotics and related drugs) in seven European electronic healthcare databases: a cross-national descriptive study from the PROTECT-EU project. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2016;25:56–65. doi: 10.1002/pds.3825. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases