Rethinking Communication in the Immune System: The Quorum Sensing Concept
- PMID: 30611647
- PMCID: PMC6619492
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2018.12.002
Rethinking Communication in the Immune System: The Quorum Sensing Concept
Abstract
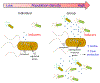
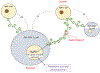
Quorum sensing was first described as the communication process bacteria employ to coordinate changes in gene expression and therefore, their collective behavior in response to population density. Emerging new evidence suggests that quorum sensing can also contribute to the regulation of immune cell responses. Quorum sensing might be achieved by the ability of immune cells to perceive the density of their own populations or those of other cells in their environment; responses to alterations in cell density might then be coordinated via changes in gene expression and protein signaling. Quorum sensing mechanisms can regulate T and B cell as well as macrophage function. We posit that perturbations in quorum sensing may undermine the balance between diverse immune cell populations and predispose the host to immune abnormalities.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

