Five-Year Outcomes of a Phase 1 Dose-Escalation Study Using Stereotactic Body Radiosurgery for Patients With Low-Risk and Intermediate-Risk Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 30611838
- PMCID: PMC7525798
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.12.045
Five-Year Outcomes of a Phase 1 Dose-Escalation Study Using Stereotactic Body Radiosurgery for Patients With Low-Risk and Intermediate-Risk Prostate Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: To report toxicity outcomes, prostate-specific antigen (PSA) relapse, and cumulative incidence posttreatment biopsy results among patients treated on a prospective dose escalation study using ultra-hypofractionated stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for patients with low- and intermediate-risk prostate cancer.
Methods and materials: A total of 136 patients were enrolled in a phase 1 dose-escalation study to determine the tolerance of escalating radiation dose levels of SBRT for the treatment of localized prostate cancer. The initial dose level was 32.5 Gy in 5 fractions, and doses were then sequentially escalated to 35 Gy, 37.5 Gy, and 40 Gy. Eligibility criteria included only patients with low and intermediate risk, and the maximum prostate volume was 60 cm3. Patients treated with neoadjuvant androgen deprivation were excluded. The median follow-up in survivors for the 4 dose levels was 5.9, 5.4, 4.1, and 3.5 years, respectively.
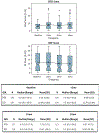
Results: The incidence of acute grade 2 rectal toxicities for dose levels 1 to 4 were 0%, 2.9%, 2.8%, and 11.4% respectively. No grade 3 or 4 acute rectal toxicities were observed. The incidence of acute grade 2 urinary toxicities for dose levels 1 to 4 were 16.7%, 22.9%, 8.3%, and 17.1%, respectively. No grade 3 or 4 acute urinary toxicities were observed. No grade 2 or higher rectal toxicities were observed. The incidence of late grade 2 urinary toxicities for dose levels 1 to 4 was 23.3%, 25.7%, 27.8%, and 31.4%, respectively. Only 1 late grade 3 urinary toxicity (urethral stricture) developed in the 40-Gy dose arm; the stricture was corrected with transurethral resection. No grade 4 late urinary toxicity was observed. The 5-year cumulative incidence of prostate-specific antigen failure for dose levels 1 to 4 was 15%, 6%, 0%, and 0%. The incidence of a 2-year positive posttreatment biopsy was 47.6%, 19.2%, 16.7%, and 7.7%, respectively for the 4 dose arms (P = .013).
Conclusions: SBRT doses ranging from 32.5 to 40 Gy in 5 fractions were well tolerated without severe urinary or rectal toxicities. Biopsy outcomes suggest improved rates of tumor clearance observed with higher doses.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: M.J.Z. serves as a consultant for Augmenix.
Figures
References
-
- King CR, Freeman D, Kaplan I, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer: Pooled analysis from a multi-institutional consortium of prospective phase II trials. Radiother Oncol 2013;109:217–221. - PubMed
-
- King CR, Brooks JD, Gill H, et al. Long-term outcomes from a prospective trial of stereotactic body radiotherapy for low-risk prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2012;82:877–882. - PubMed
-
- Henderson DR, Tree AC, van As NJ. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for prostate cancer. Clin Oncol 2015;27:270–279. - PubMed
-
- Mantz C A phase II trial of stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy for low-risk prostate cancer using a non-robotic linear accelerator and real-time target tracking: Report of toxicity, quality of life, and disease control outcomes with 5-year minimum follow-up. Front Oncol 2014; 4:279. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous