Association Between Wait Time for Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement and Early Postprocedural Outcomes
- PMID: 30612506
- PMCID: PMC6405724
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.118.010407
Association Between Wait Time for Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement and Early Postprocedural Outcomes
Abstract
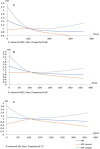
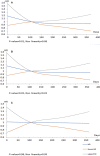
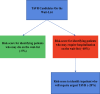
Background Rapid growth in transcatheter aortic valve replacement ( TAVR ) demand has translated to inadequate access, reflected by prolonged wait times. Increasing wait times are associated with important adverse outcomes while on the wait-list; however, it is unknown if prolonged wait times influence postprocedural outcomes. Our objective was to determine the association between TAVR wait times and postprocedural outcomes. Methods and Results In this population-based study in Ontario, Canada, we identified all TAVR procedures between April 1, 2010, and March 31, 2016. Wait time was defined as the number of days between initial referral and the procedure. Primary outcomes of interest were 30-day all-cause mortality and all-cause readmission. Multivariable regression models incorporated wait time as a nonlinear variable, using cubic splines. The study cohort included 2170 TAVR procedures, of which 1741 cases were elective and 429 were urgent. There was a significant, nonlinear relationship between TAVR wait time and post- TAVR 30-day mortality, as well as 30-day readmission. We observed an increased hazard associated with shorter wait times that diminished as wait times increased. This statistically significant nonlinear relationship was seen in the unadjusted model as well as after adjusting for clinical variables. However, after adjusting for case urgency status, there was no relationship between wait times and postprocedural outcomes. In sensitivity analyses restricted to either only elective or only urgent cases, there was no relationship between wait times and postprocedural outcomes. Conclusions Wait time has a complex relationship with postprocedural outcomes that is mediated entirely by urgency status. This suggests that further research should elucidate factors that predict hospitalization requiring urgent TAVR while on the wait list.
Keywords: outcome; transcatheter aortic valve implantation; transcatheter aortic valve replacement; wait time.
Figures

Comment in
-
Treating Symptomatic Aortic Stenosis With Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement: Is There Time to Wait?J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Jan 8;8(1):e011527. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.011527. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019. PMID: 30612523 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Barbanti M, Webb JG, Gilard M, Capodanno D, Tamburino C. Transcatheter aortic valve implantation in 2017: state of the art. EuroIntervention. 2017;13:AA11–AA21. - PubMed
-
- Falk V, Baumgartner H, Bax JJ, De Bonis M, Hamm C, Holm PJ, Iung B, Lancellotti P, Lansac E, Munoz DR, Rosenhek R, Sjogren J, Tornos Mas P, Vahanian A, Walther T, Wendler O, Windecker S, Zamorano JL; ESC Scientific Document Group . 2017 ESC/EACTS guidelines for the management of valvular heart disease. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2017;52:616–664. - PubMed
-
- Elbaz‐Greener G, Masih S, Fang J, Ko DT, Lauck SB, Webb JG, Nallamothu BK, Wijeysundera HC. Temporal trends and clinical consequences of wait‐times for trans‐catheter aortic valve replacement: a population based study. Circulation. 2018;138:483–493. - PubMed
-
- Wijeysundera HC, Wong WW, Bennell MC, Fremes SE, Radhakrishnan S, Peterson M, Ko DT. Impact of wait times on the effectiveness of transcatheter aortic valve replacement in severe aortic valve disease: a discrete event simulation model. Can J Cardiol. 2014;30:1162–1169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

