Effect of Combined Therapy of Robot and Low-Frequency Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation on Hemispatial Neglect in Stroke Patients
- PMID: 30613071
- PMCID: PMC6325312
- DOI: 10.5535/arm.2018.42.6.788
Effect of Combined Therapy of Robot and Low-Frequency Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation on Hemispatial Neglect in Stroke Patients
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effect of upper limb rehabilitation combining robot with low-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) on unilateral spatial neglect in stroke patients.
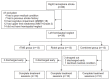
Methods: Patients who had hemispatial neglect after right hemisphere stroke were randomly divided into rTMS only group, robot only group, and combined group. All groups received conventional neglect therapy and additional treatment for each group. rTMS group received rTMS therapy. Robot group received robot therapy, while combined group received both therapies. The effect of therapy was assessed with Motor-Free Visual Perception Test-3 (MVPT-3), line bisection test, star cancellation test, Catherine Bergego Scale (CBS), Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE), and the Korean version of Modified Barthel Index (K-MBI). These measurements were evaluated before and after treatment.
Results: For each group, 10 patients were recruited. There were no significant differences in baseline characteristics or initial values among the three groups. Two weeks after the therapy, all groups showed significant improvement in MVPT-3, line bisection test, star cancellation test, CBS, MMSE, and K-MBI. However, changes in measurements showed no significant differences among groups.
Conclusion: Treatment effect of the combined therapy of robotic therapy and low-frequency rTMS therapy for hemispatial neglect was not statistically different from that of each single treatment. Results of this study did not prove the superiority of any of the three treatments. Further study with large number of patients is needed to evaluate the superiority of these treatments.
Keywords: Perceptual disorders; Rehabilitation; Robotics; Stroke; Transcranial magnetic stimulation.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures


References
-
- Luaute J, Halligan P, Rode G, Rossetti Y, Boisson D. Visuo-spatial neglect: a systematic review of current interventions and their effectiveness. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2006;30:961–82. - PubMed
-
- Pierce SR, Buxbaum LJ. Treatments of unilateral neglect: a review. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2002;83:256–68. - PubMed
-
- Heilman KM, Valenstein E. Frontal lobe neglect in man. Neurology. 1972;22:660–4. - PubMed
-
- Watson RT, Heilman KM. Thalamic neglect. Neurology. 1979;29:690–4. - PubMed
-
- Damasio AR, Damasio H, Chui HC. Neglect following damage to the frontal lobe or basal ganglia. Neuropsychologia. 1980;18:123–32. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

