Management of osteitis pubis in athletes: rehabilitation and return to training - a review of the most recent literature
- PMID: 30613167
- PMCID: PMC6307487
- DOI: 10.2147/OAJSM.S155077
Management of osteitis pubis in athletes: rehabilitation and return to training - a review of the most recent literature
Abstract
Osteitis pubis is a common cause of chronic groin pain, especially in athletes. Although a precise etiology is not defined, it seems to be related to muscular imbalance and pelvic instability. Diagnosis is based on detailed history, clinical evaluation, and imaging, which are crucial for a correct diagnosis and proper management. Many different therapeutic approaches have been proposed for osteitis pubis; conservative treatment represents the first-line approach and provides good results in most patients, especially if based on an individualized multimodal rehabilitative management. Different surgical options have been also described, but they should be reserved to recalcitrant cases. In this review, a critical analysis of the literature about athletic osteitis pubis is performed, especially focusing on its diagnostic and therapeutic management.
Keywords: groin pain; osteitis pubis; pubalgia; rehabilitation; review.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
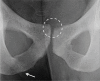

References
-
- Verrall GM, Hamilton IA, Slavotinek JP, et al. Hip joint range of motion reduction in sports-related chronic groin injury diagnosed as pubic bone stress injury. J Sci Med Sport. 2005;8(1):77–84. - PubMed
-
- Harmon KG. Evaluation of groin pain in athletes. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2007;6(6):354–361. - PubMed
-
- DeVries JG, Berlet GC. Understanding levels of evidence for scientific communication. Foot Ankle Spec. 2010;3(4):205–209. - PubMed
-
- Ekstrand J, Hilding J. The incidence and differential diagnosis of acute groin injuries in male soccer players. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 1999;9(2):98–103. - PubMed

