BPI-9016M, a c-Met inhibitor, suppresses tumor cell growth, migration and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma via miR203-DKK1
- PMID: 30613269
- PMCID: PMC6299440
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.27667
BPI-9016M, a c-Met inhibitor, suppresses tumor cell growth, migration and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma via miR203-DKK1
Abstract
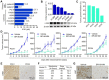
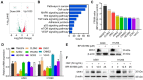
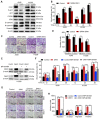
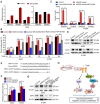
Activation of c-Met plays a critical role in tumorigenesis, migration and invasion in lung cancer. Here, we explored the therapeutic efficacy of a novel small-molecule c-Met inhibitor (BPI-9016M) in lung adenocarcinoma and investigated the underlying molecular mechanisms. Method: BPI-9016M, a c-Met tyrosine kinase receptor inhibitor, was used to treat patient-derived xenografts (PDX) from lung adenocarcinoma in NOD/SCID mice. Immunohistochemistry and Western blot analysis were used to determine the expression of c-Met and its downstream signaling molecules. CCK8, wound healing, and trans-well assays were used to analyze cell proliferation, spreading, migration and invasion. RNA sequencing and quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) was used to screen and validate the expression of downstream genes in lung adenocarcinoma cells treated with BPI-9016M. Luciferase reporter assay was used to detect the interaction between miRNA and the targeted gene. Results: BPI-9016M significantly suppressed growth in three out of four lung adenocarcinoma PDX models, particularly in the tumors with high expression of c-Met. In lung adenocarcinoma cell lines, BPI-9016M treatment resulted in increased miR203, which reduced migration and invasion and also repressed Dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1) expression. Forced overexpression of DKK1 or down-regulation of miR203 reversed the inhibitory effect of BPI-9016M on migration and invasion. C-Met was verified to positively and negatively associate with DKK1 and miR203, respectively. High expression of c-Met/DKK1 or low expression of miR203 related to poor outcome of lung adenocarcinoma patients. Furthermore, we observed significantly enhanced tumor cell growth inhibition upon combining BPI-9016M treatment with miR203 mimics or DKK1 siRNA. Conclusion: Our data indicated that BPI-9016M is an effective agent against lung adenocarcinoma, particularly in tumors with c-Met activation, and likely functions through upregulation of miR203 leading to reduced DKK1 expression.
Keywords: BPI-9016M; Dickkopf-1 (DKK1); c-Met; lung adenocarcinoma; miR203.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Trusolino L, Bertotti A, Comoglio PM. MET signalling: principles and functions in development, organ regeneration and cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11:834–48. - PubMed
-
- Gherardi E, Birchmeier W, Birchmeier C, Vande Woude G. Targeting MET in cancer: rationale and progress. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12:89–103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

