PET-MR and SPECT-MR multimodality probes: Development and challenges
- PMID: 30613293
- PMCID: PMC6299694
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.26610
PET-MR and SPECT-MR multimodality probes: Development and challenges
Abstract
Positron emission tomography (PET)-magnetic resonance (MR) or single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)-MR hybrid imaging is being used in daily clinical practice. Due to its advantages over stand-alone PET, SPECT or MR imaging, in many areas such as oncology, the demand for hybrid imaging techniques is increasing dramatically. The use of multimodal imaging probes or biomarkers in a single molecule or particle to characterize the imaging subjects such as disease tissues certainly provides us with more accurate diagnosis and promotes therapeutic accuracy. A limited number of multimodal imaging probes are being used in preclinical and potential clinical investigations. The further development of multimodal PET-MR and SPECT-MR imaging probes includes several key elements: novel synthetic strategies, high sensitivity for accurate quantification and high anatomic resolution, favourable pharmacokinetic profile and target-specific binding of a new probe. This review thoroughly summarizes all recently available and noteworthy PET-MR and SPECT-MR multimodal imaging probes including small molecule bimodal probes, nano-sized bimodal probes, small molecular trimodal probes and nano-sized trimodal probes. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first comprehensive overview of all PET-MR and SPECT-MR multimodal probes. Since the development of multimodal PET-MR and SPECT-MR imaging probes is an emerging research field, a selection of 139 papers were recognized following the literature review. The challenges for designing multimodal probes have also been addressed in order to offer some future research directions for this novel interdisciplinary research field.
Keywords: PET-MR; SPECT-MR; bimodality imaging probe; contrast agent; radioligand.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


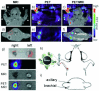
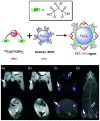
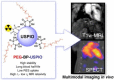


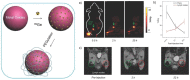
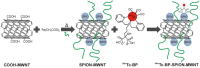

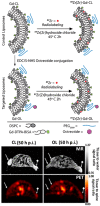
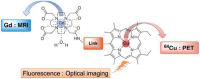

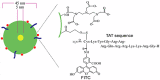
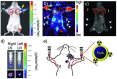

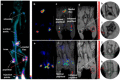
References
-
- Mankoff DA. A definition of molecular imaging. J Nucl Med. 2007;48(N):18–21. - PubMed
-
- Markus R. Molecular imaging: basic principles and applications in biomedical research: World Scientific. 2013.
-
- Massoud TF, Gambhir SS. Molecular imaging in living subjects: seeing fundamental biological processes in a new light. Genes Dev. 2003;17:545–80. - PubMed
-
- Masters BR. Molecular Fluorescence: Principles and Applications. J Biomed Opt. 2013;18:039901.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

