Rapid isotopic exchange in nanoparticles
- PMID: 30613775
- PMCID: PMC6314871
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aau7555
Rapid isotopic exchange in nanoparticles
Abstract
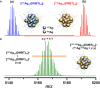
Rapid solution-state exchange dynamics in nanoscale pieces of matter is revealed, taking isotopically pure atomically precise clusters as examples. As two isotopically pure silver clusters made of 107Ag and 109Ag are mixed, an isotopically mixed cluster of the same entity results, similar to the formation of HDO, from H2O and D2O. This spontaneous process is driven by the entropy of mixing and involves events at multiple time scales.
Figures



References
-
- Urey H. C., Brickwedde F. G., Murphy G. M., A hydrogen isotope of mass 2. Phys. Rev. 39, 164–165 (1932).
-
- Lewis G. N., Macdonald R. T., Concentration of H2 isotope. J. Chem. Phys. 1, 341–344 (1933).
-
- Thibblin A., Ahlberg P., Reaction branching and extreme kinetic isotope effects in the study of reaction mechanisms. Chem. Soc. Rev. 18, 209–224 (1989).
-
- Pyper J. W., Newbury R. S., Barton G. W. Jr., Study of the isotopic disproportionation reaction between light and heavy water using a pulsed-molecular-beam mass spectrometer. J. Chem. Phys. 46, 2253–2257 (1967).
-
- Park S.-C., Jung K.-H., Kang H., H/D isotopic exchange between water molecules at ice surfaces. J. Chem. Phys. 121, 2765–2774 (2004). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

