Differentially Branched Ester Amine Quadpolymers with Amphiphilic and pH-Sensitive Properties for Efficient Plasmid DNA Delivery
- PMID: 30615464
- PMCID: PMC7297465
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b00963
Differentially Branched Ester Amine Quadpolymers with Amphiphilic and pH-Sensitive Properties for Efficient Plasmid DNA Delivery
Abstract
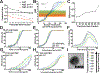
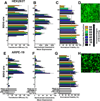
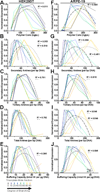
Development of highly effective nonviral gene delivery vectors for transfection of diverse cell populations remains a challenge despite utilization of both rational and combinatorial driven approaches to nanoparticle engineering. In this work, multifunctional polyesters are synthesized with well-defined branching structures via A2 + B2/B3 + C1 Michael addition reactions from small molecule acrylate and amine monomers and then end-capped with amine-containing small molecules to assess the influence of polymer branching structure on transfection. These Branched poly(Ester Amine) Quadpolymers (BEAQs) are highly effective for delivery of plasmid DNA to retinal pigment epithelial cells and demonstrate multiple improvements over previously reported leading linear poly(beta-amino ester)s, particularly for volume-limited applications where improved efficiency is required. BEAQs with moderate degrees of branching are demonstrated to be optimal for delivery under high serum conditions and low nanoparticle doses further relevant for therapeutic gene delivery applications. Defined structural properties of each polymer in the series, including tertiary amine content, correlated with cellular transfection efficacy and viability. Trends that can be applied to the rational design of future generations of biodegradable polymers are elucidated.
Keywords: branched polymer, plasmid DNA; nonviral, gene delivery; polymeric nanoparticle; transfection.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Reducible Branched Ester-Amine Quadpolymers (rBEAQs) Codelivering Plasmid DNA and RNA Oligonucleotides Enable CRISPR/Cas9 Genome Editing.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019 Mar 20;11(11):10472-10480. doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b20206. Epub 2019 Mar 8. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019. PMID: 30794383 Free PMC article.
-
The transition from linear to highly branched poly(β-amino ester)s: Branching matters for gene delivery.Sci Adv. 2016 Jun 17;2(6):e1600102. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1600102. eCollection 2016 Jun. Sci Adv. 2016. PMID: 27386572 Free PMC article.
-
A versatile family of degradable non-viral gene carriers based on hyperbranched poly(ester amine)s.J Control Release. 2005 Dec 5;109(1-3):317-29. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2005.06.022. Epub 2005 Aug 2. J Control Release. 2005. PMID: 16081184
-
Michael Addition Polymerization of Trifunctional Amine and Acrylic Monomer: A Versatile Platform for Development of Biomaterials.Biomacromolecules. 2016 Oct 10;17(10):3115-3126. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.6b01043. Epub 2016 Sep 15. Biomacromolecules. 2016. PMID: 27599254 Review.
-
Poly(β-amino ester)-based gene delivery systems: From discovery to therapeutic applications.J Control Release. 2019 Sep 28;310:155-187. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.08.024. Epub 2019 Aug 24. J Control Release. 2019. PMID: 31454533 Review.
Cited by
-
Polymeric nanoparticles for dual-targeted theranostic gene delivery to hepatocellular carcinoma.Sci Adv. 2022 Jul 22;8(29):eabo6406. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abo6406. Epub 2022 Jul 20. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35857843 Free PMC article.
-
Poly(Beta-Amino Ester) Nanoparticles Enable Nonviral Delivery of CRISPR-Cas9 Plasmids for Gene Knockout and Gene Deletion.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020 Jun 5;20:661-672. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.04.005. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020. PMID: 32380416 Free PMC article.
-
A Polymeric Nanoparticle Formulation for Targeted mRNA Delivery to Fibroblasts.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Feb;10(5):e2205475. doi: 10.1002/advs.202205475. Epub 2022 Dec 18. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 36529964 Free PMC article.
-
Biomaterial-based gene therapy.MedComm (2020). 2023 Jun 3;4(3):e259. doi: 10.1002/mco2.259. eCollection 2023 Jun. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 37284583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Automation and data-driven design of polymer therapeutics.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021 Apr;171:1-28. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2020.11.009. Epub 2020 Nov 24. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021. PMID: 33242537 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

