Multiplex Quantitative Analysis of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Immunotherapy Outcome in Metastatic Melanoma
- PMID: 30617133
- PMCID: PMC6467753
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-2652
Multiplex Quantitative Analysis of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Immunotherapy Outcome in Metastatic Melanoma
Abstract
Purpose: Because durable response to programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) inhibition is limited to a subset of melanoma patients, new predictive biomarkers could have clinical utility. We hypothesize that pretreatment tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) profiles could be associated with response.
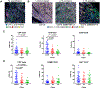
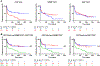
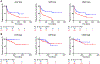
Experimental design: Pretreatment whole tissue sections from 94 melanoma patients treated with anti-PD-1 therapy were profiled by multiplex immunofluorescence to perform TIL quantification (CD4, CD8, CD20) and assess TIL activation (CD3, GZMB, Ki67). Two independent image analysis technologies were used: inForm (PerkinElmer) to determine cell counts, and AQUA to measure protein by quantitative immunofluorescence (QIF). TIL parameters by both methodologies were correlated with objective response or disease control rate (ORR/DCR) by RECIST 1.1 and survival outcome.
Results: Pretreatment lymphocytic infiltration, by cell counts or QIF, was significantly higher in complete or partial response than in stable or progressive disease, particularly for CD8 (P < 0.0001). Neither TIL activation nor dormancy was associated with outcome. CD8 associations with progression-free survival (HR > 3) were independently significant in multivariable analyses and accounted for similar CD3 associations in anti-PD-1-treated patients. CD8 was not associated with melanoma prognosis in the absence of immunotherapy. Predictive performance of CD8 cell count (and QIF) had an area under the ROC curve above 0.75 (ORR/DCR), which reached 0.83 for ipilimumab plus nivolumab.
Conclusions: Pretreatment lymphocytic infiltration is associated with anti-PD-1 response in metastatic melanoma. Quantitative TIL analysis has potential for application in digital precision immuno-oncology as an "indicative" companion diagnostic.
©2019 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential Conflicts:
H. Kluger has served as a consultant for Corvus, Nektar, Biodesix, Genetech, Pfizer, Merck and Celldex, and has received research support from Merck, Apexigen and Bristol-Meyers Squibb
D. Rimm has served as a consultant, advisor or served on a Scientific Advisory Board for Amgen, Astra Zeneca, Agendia, Biocept, BMS, Cell Signaling Technology, Cepheid, Daiichi Sankyo, GSK, Merck, NanoString, Perkin Elmer, PAIGE, and Ultivue. He has received research funding from Astra Zeneca, Cepheid, Navigate/Novartis, NextCure, Lilly, Ultivue, and Perkin Elmer
Figures

References
-
- Weber JS, D’Angelo SP, Minor D, et al. Nivolumab versus chemotherapy in patients with advanced melanoma who progressed after anti-CTLA-4 treatment (CheckMate 037): a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(4):375–384. - PubMed
-
- Robert C, Schachter J, Long GV, et al. Pembrolizumab versus Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(26):2521–2532. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

